![figure-1-large.jpg Crystal structure of the parent compound of a calcium-strontium-based cuprate superconductor [(Ca/Sr)2CuO3]](/-/media/bes/images/highlights/2015/02/figure-1-large.jpg?h=640&w=482&la=en&hash=D1DB4EF52CFDD381CF2E3555D27C4B6F5EB9C292E8C55E49392F2B5AA679B0B5)
Predicting Magnetic Behavior in Copper Oxide Superconductors
New theoretical techniques predict experimental observations in superconducting materials.
![figure-1-large.jpg Crystal structure of the parent compound of a calcium-strontium-based cuprate superconductor [(Ca/Sr)2CuO3]](/-/media/bes/images/highlights/2015/02/figure-1-large.jpg?h=640&w=482&la=en&hash=D1DB4EF52CFDD381CF2E3555D27C4B6F5EB9C292E8C55E49392F2B5AA679B0B5)
New theoretical techniques predict experimental observations in superconducting materials.
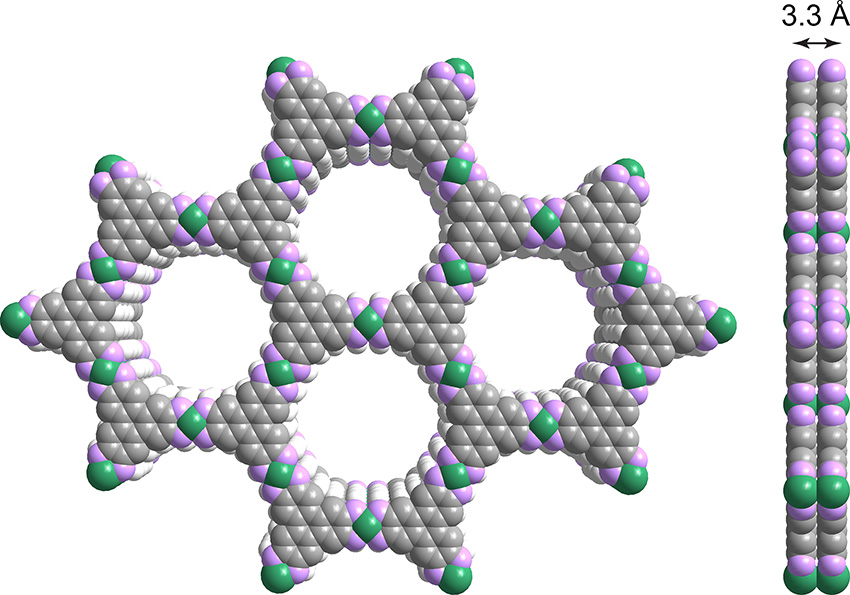
Researchers have created a porous, layered material that can serve as a graphene analog, and which may be a tool for storing energy and investigating the physics of unusual materials.
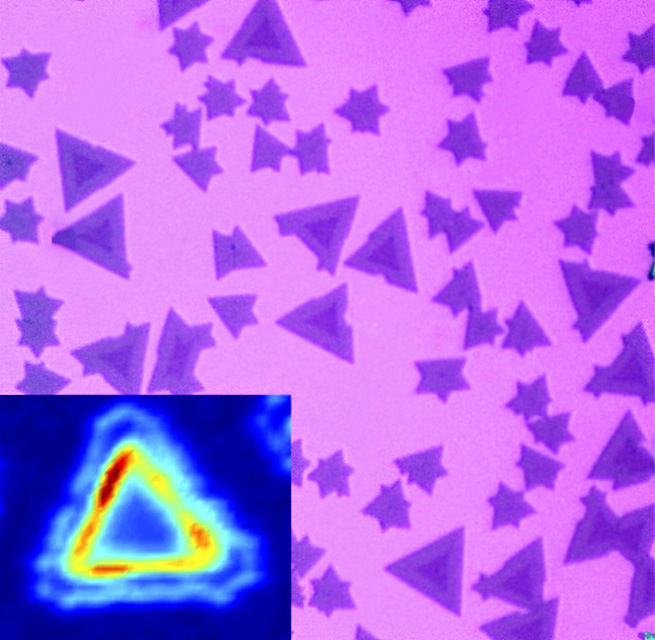
New material with a layered, atomic sandwich structure has unique optoelectronic properties.
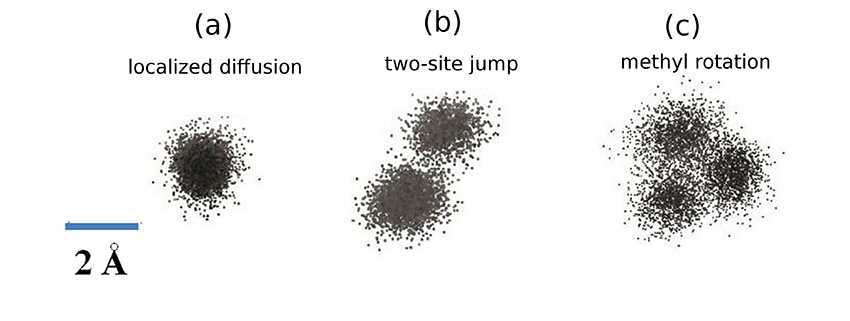
Combining computer simulations with laboratory measurements provides insights on molecular-level flexibility.
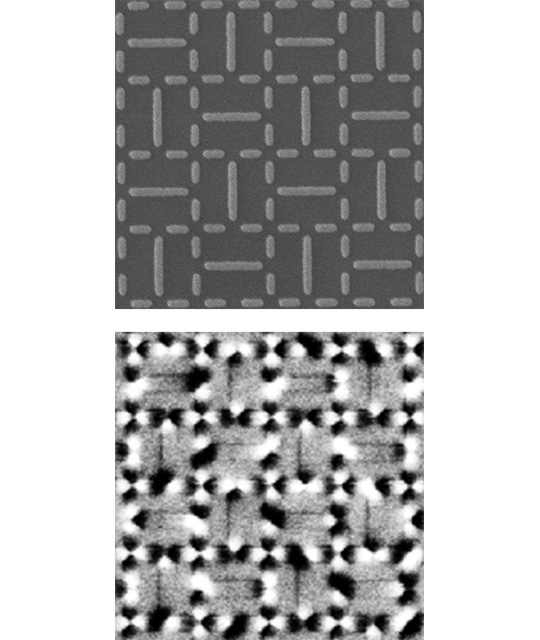
Experiments using novel magnetic nanostructures confirm theoretically predicted behavior – bolstering their utility as a tool for understanding complex magnetic materials.
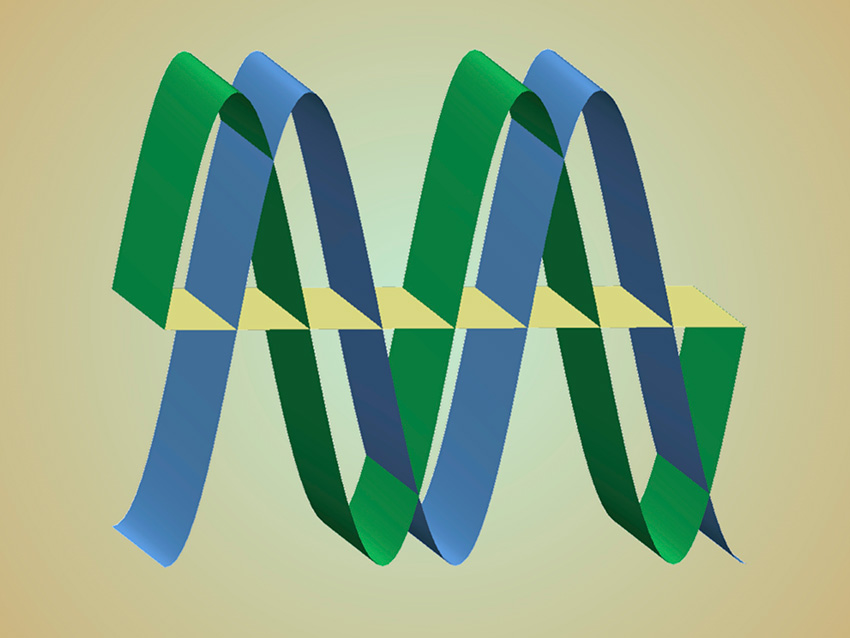
New metal oxide material works at temperatures low enough to improve fuel cell efficiency.
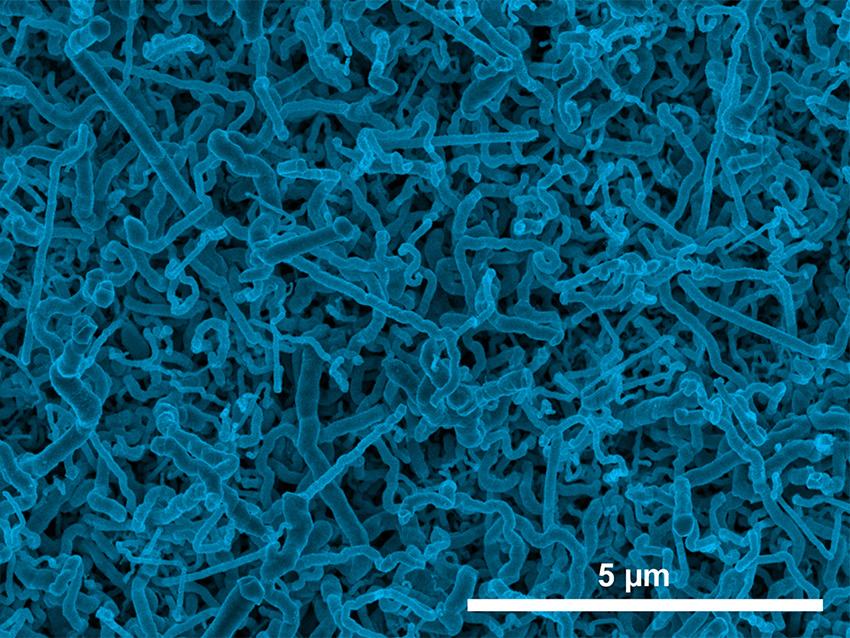
Lithium-ion batteries could benefit from this inexpensive method.
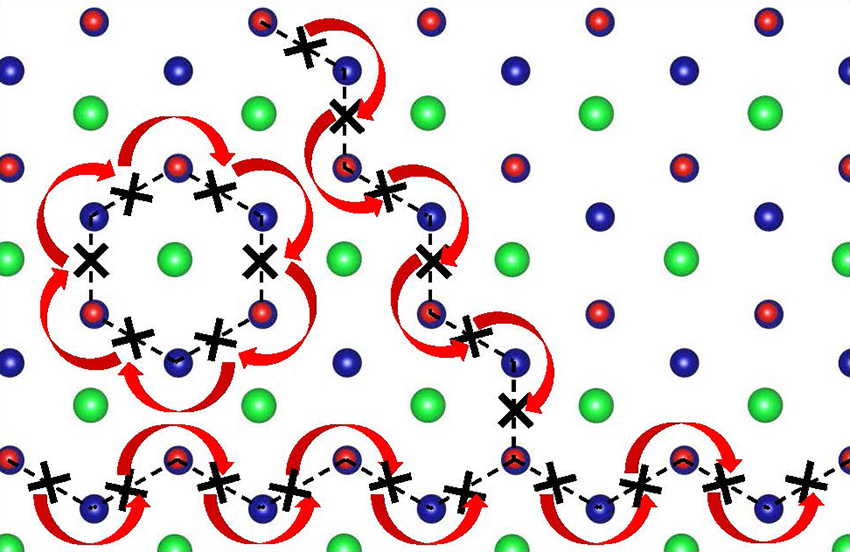
Coexistence of two states of matter that normally avoid one another is revealed by inelastic neutron scattering experiments.
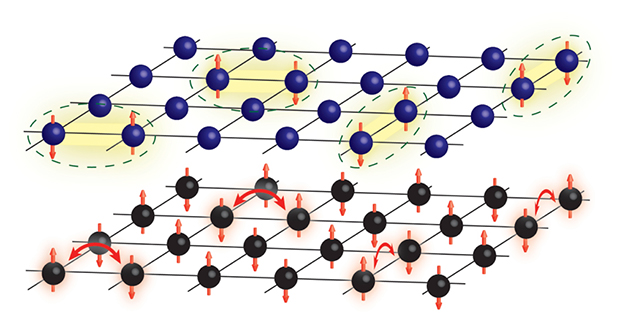
Microscopic understanding offers fresh directions for discovering new materials to transmit energy without loss.
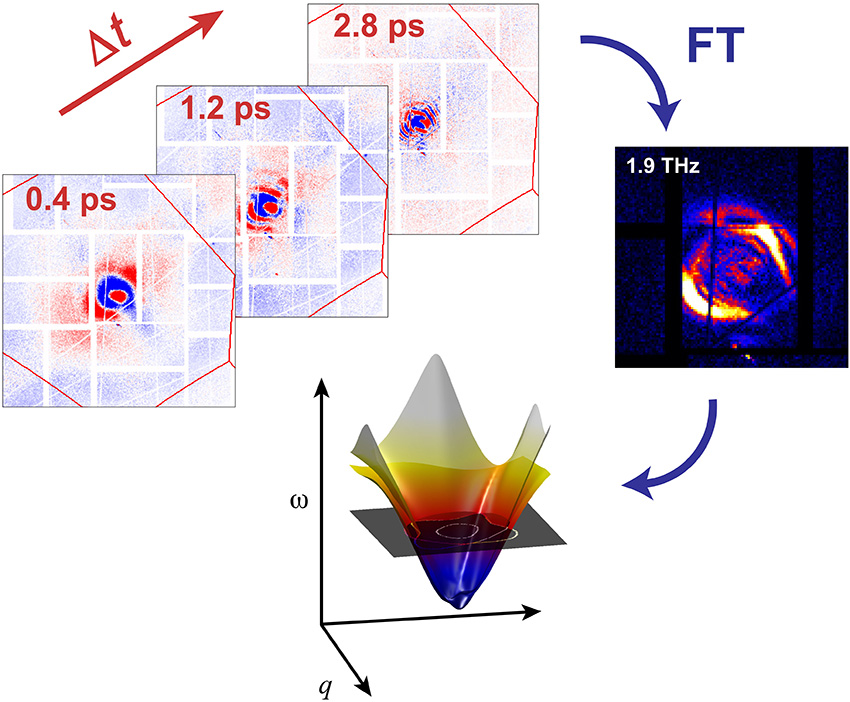
Stroboscopic x-ray pulses scatter from a vibrating crystal and reveal how energy moves.
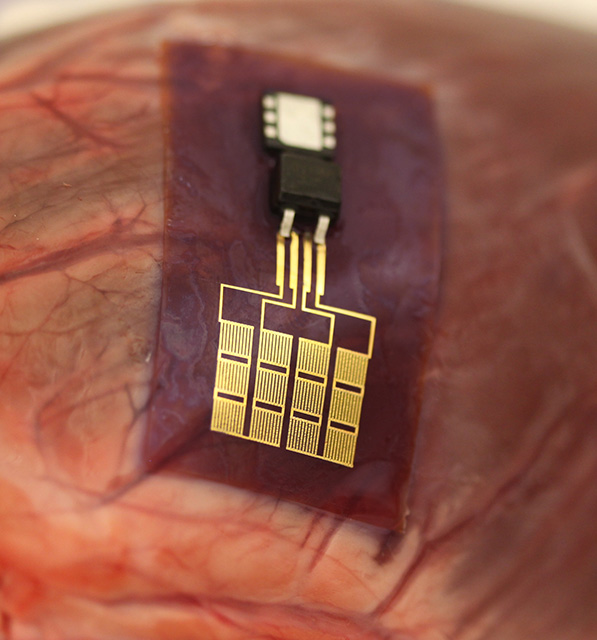
Advances in materials processing enable harvesting of energy from heartbeats.
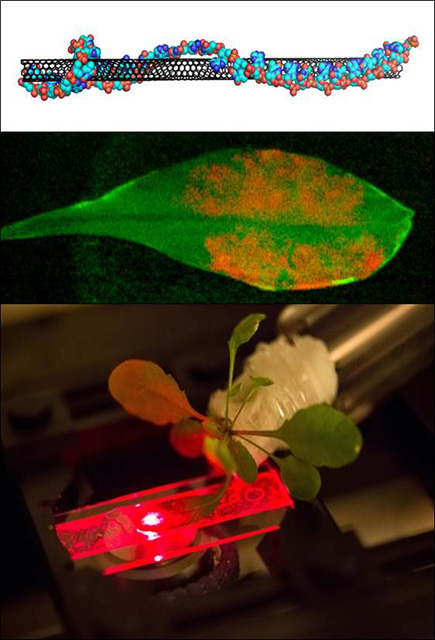

Carbon nanotubes and inorganic nanoparticles enhance photosynthetic activity and stability.