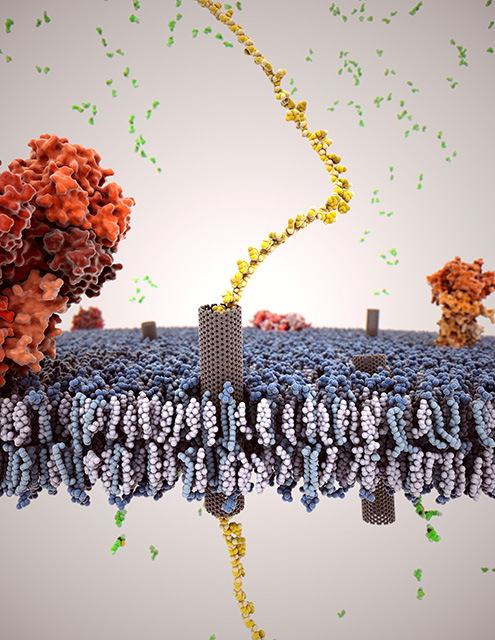
Spontaneous Formation of Biomimetic, Nanoporous Membrane Channels
Carbon nanotubes insert into artificial and active cell membranes, reproducing major features of biological channels.

Carbon nanotubes insert into artificial and active cell membranes, reproducing major features of biological channels.
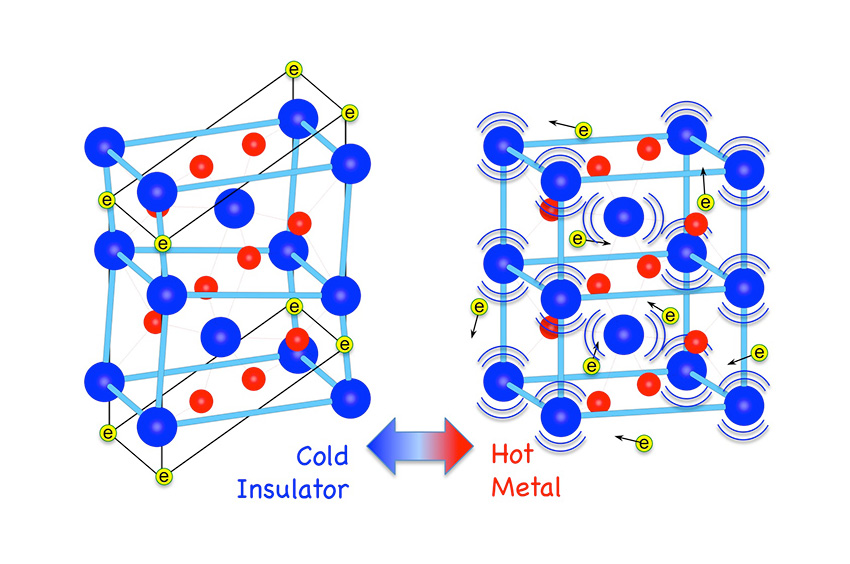
New studies explain the transition, providing a quantitative picture of a 50-year-old mystery.
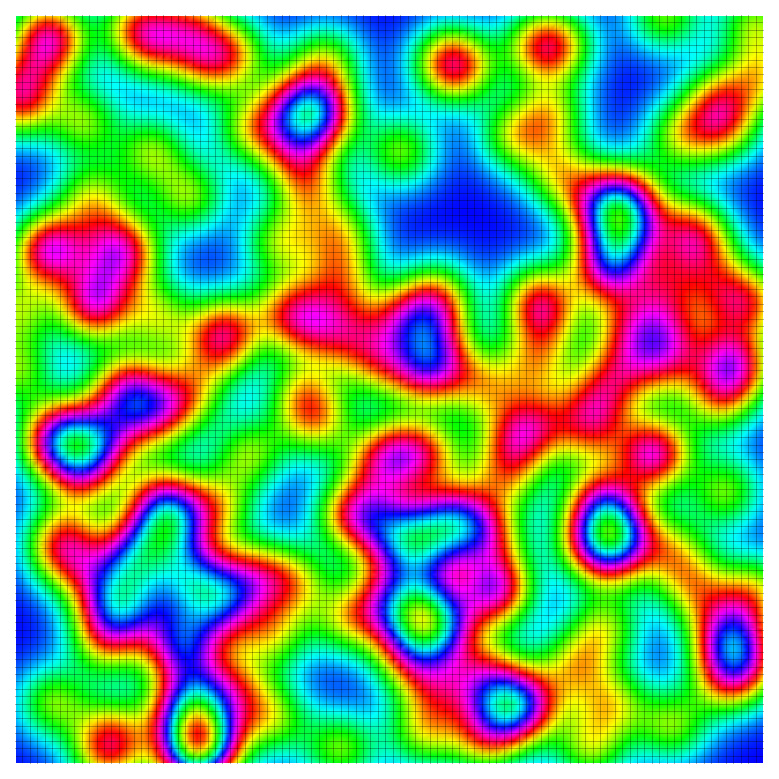
Discovery paves the way to quantitatively investigate the interplay among magnetism, superconductivity and disorder in high temperature superconductors.
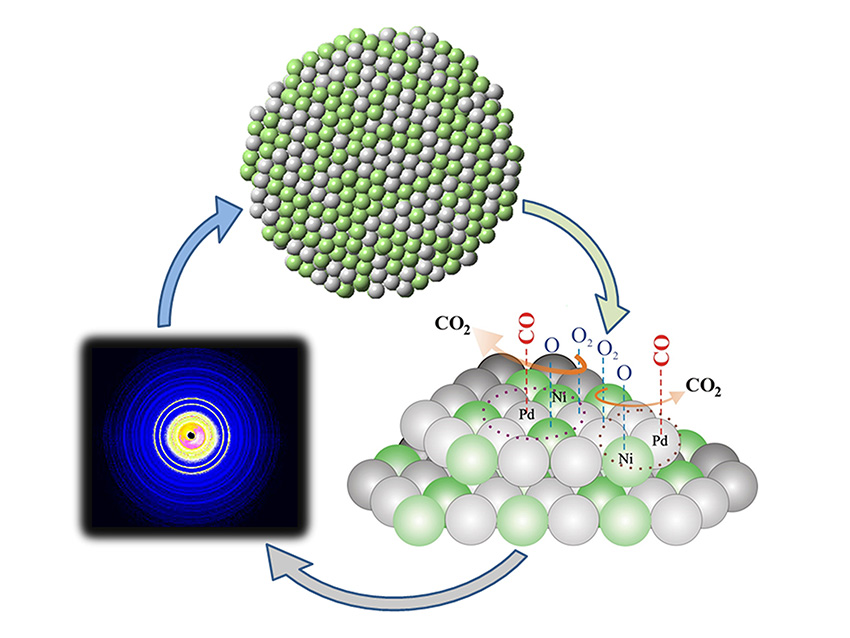
Clusters with longer separations between atoms had enhanced catalytic activity.
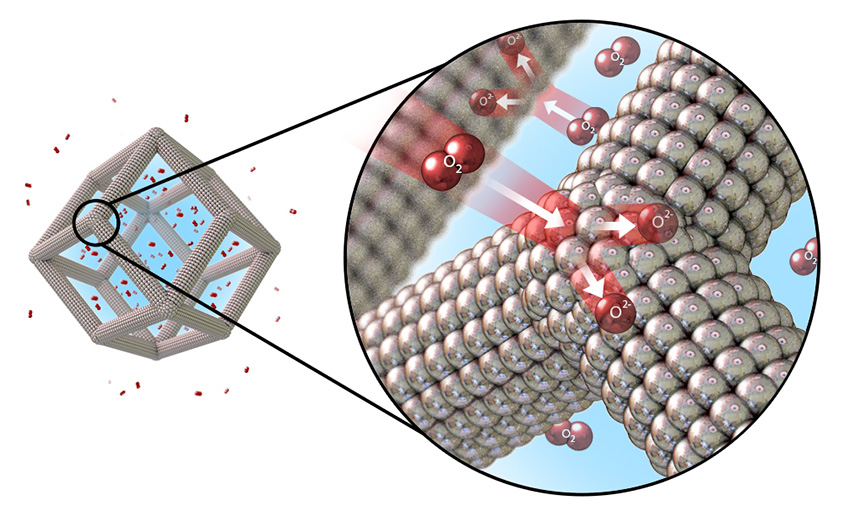
Concentrating noble-metal catalyst atoms on the surface of porous nano-frame alloys shows over thirty-fold increase in performance.
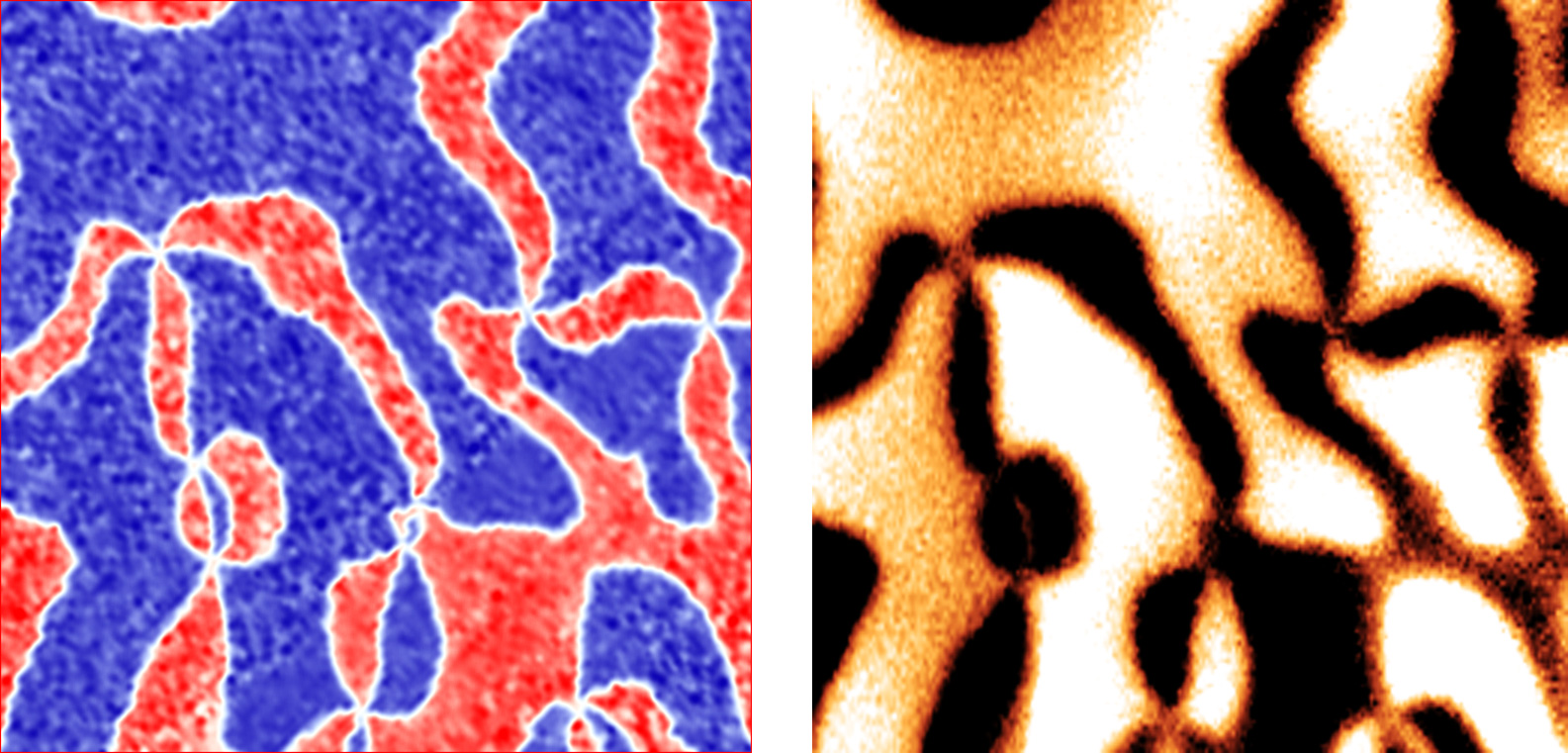
New microscopy technique reveals giant enhancement of coupling between magnetic and electric dipoles that could lead to novel electronic devices.
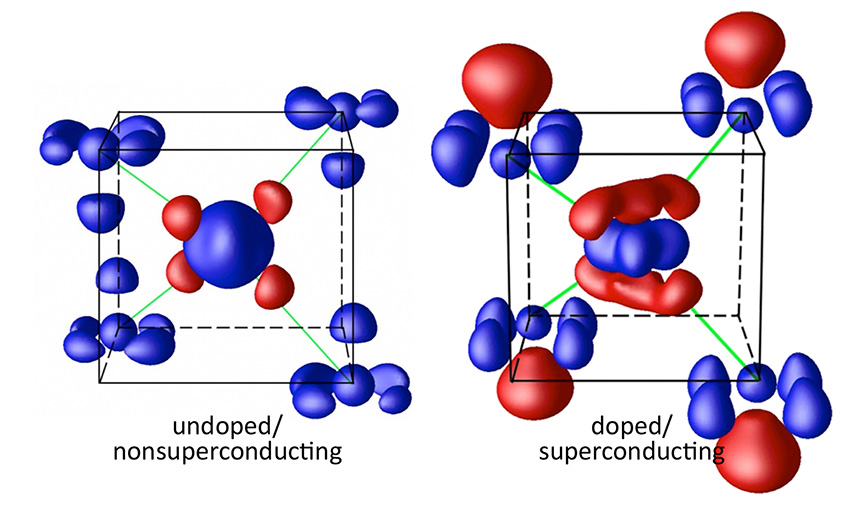
Atomic-scale details of electron distribution reveal a novel mechanism for current to flow without energy loss.
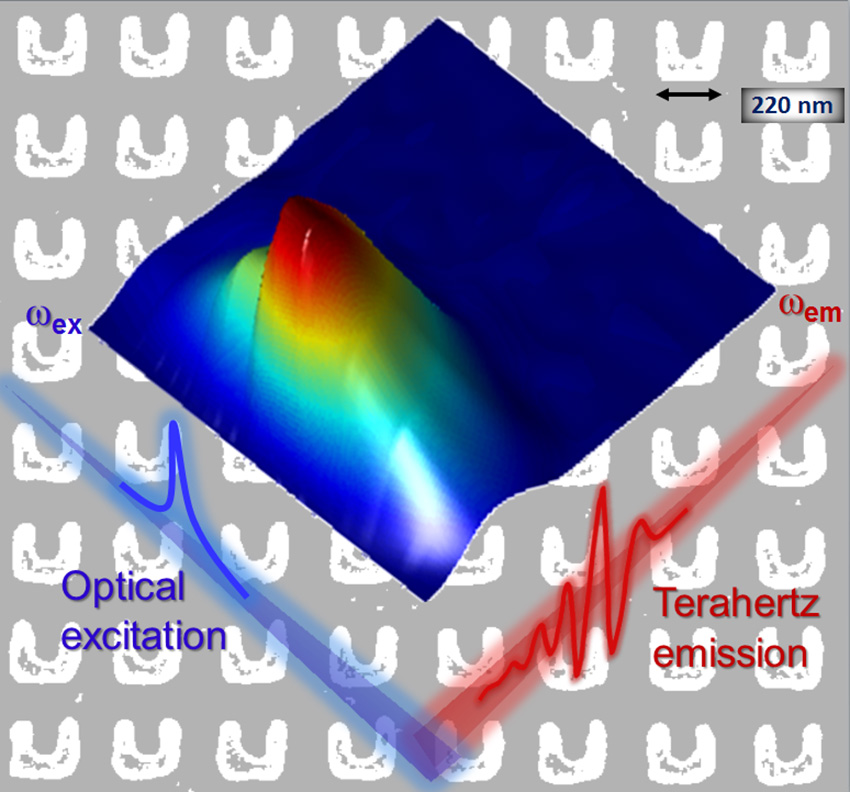
Discovery demonstrates how metamaterials may be used in non-invasive material imaging and sensing, and terahertz information technologies.
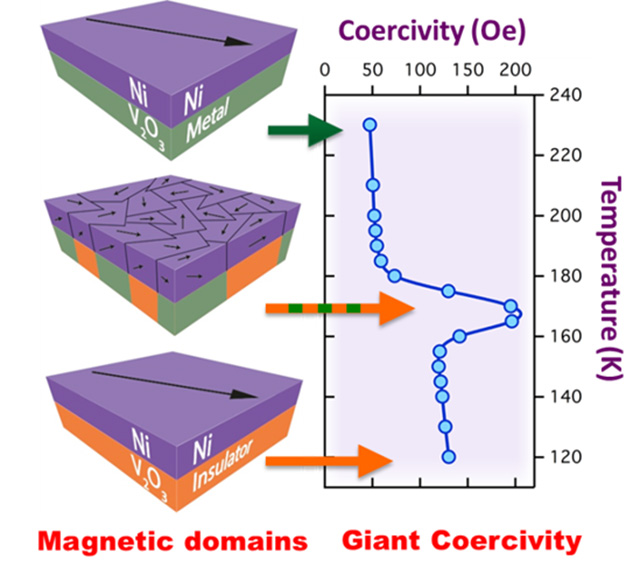
Magnetic property changes by several hundred percent over a narrow temperature range.
Tracking electronic motion in a graphene-like bulk material shows fast electrons in all dimensions.
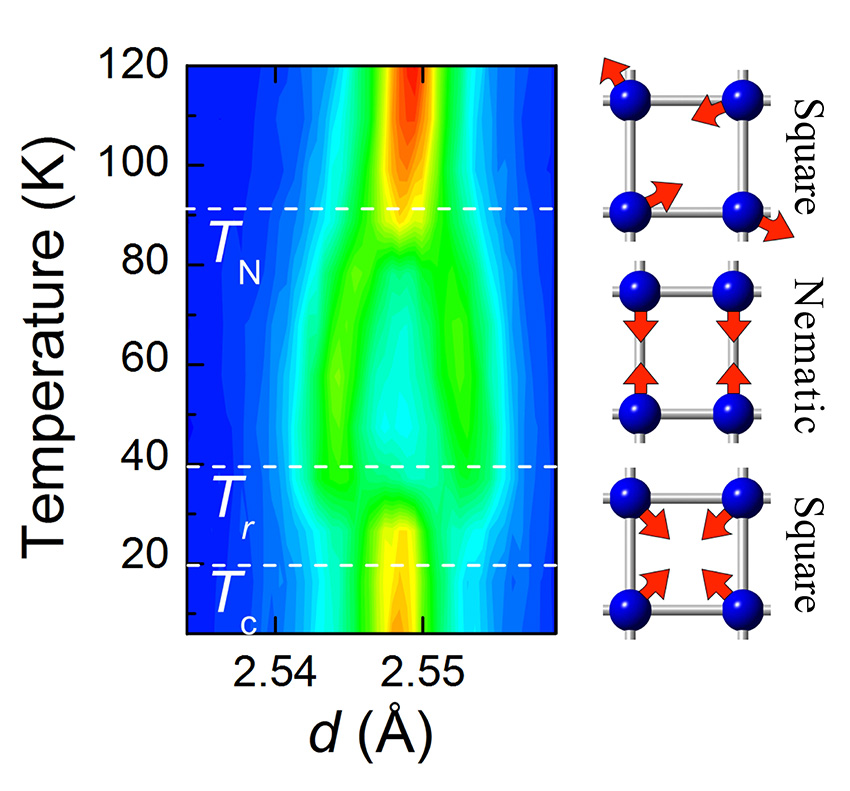
Scientists uncover the microscopic origin of a magnetic phase in iron-based superconductors.
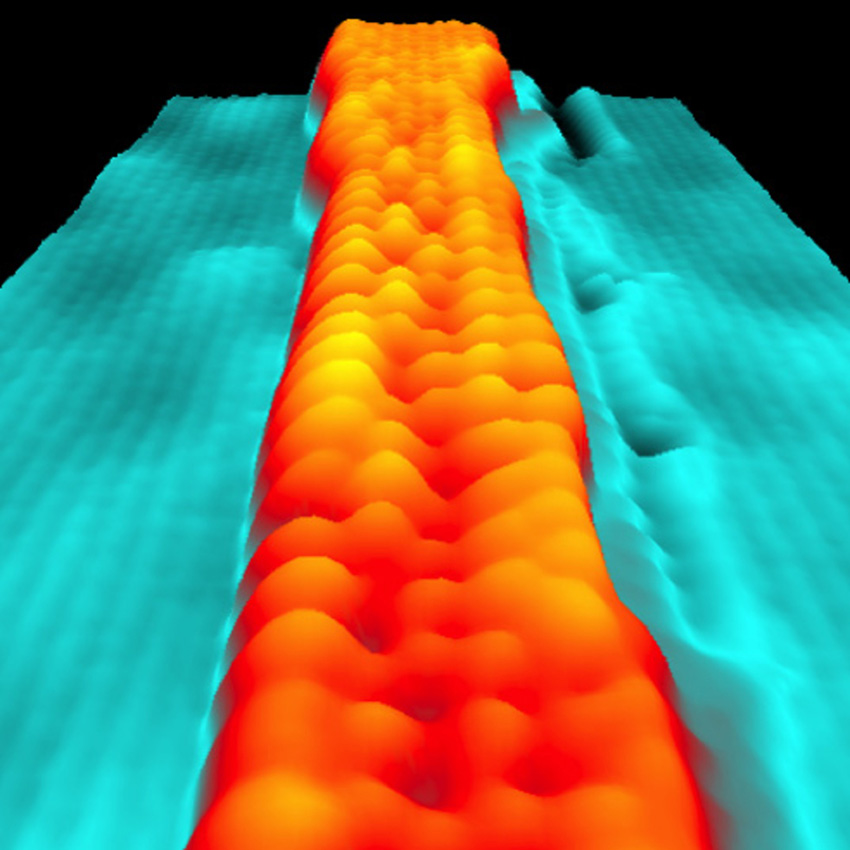
Thin widths change a high-performance electrical conductor into a semiconductor.