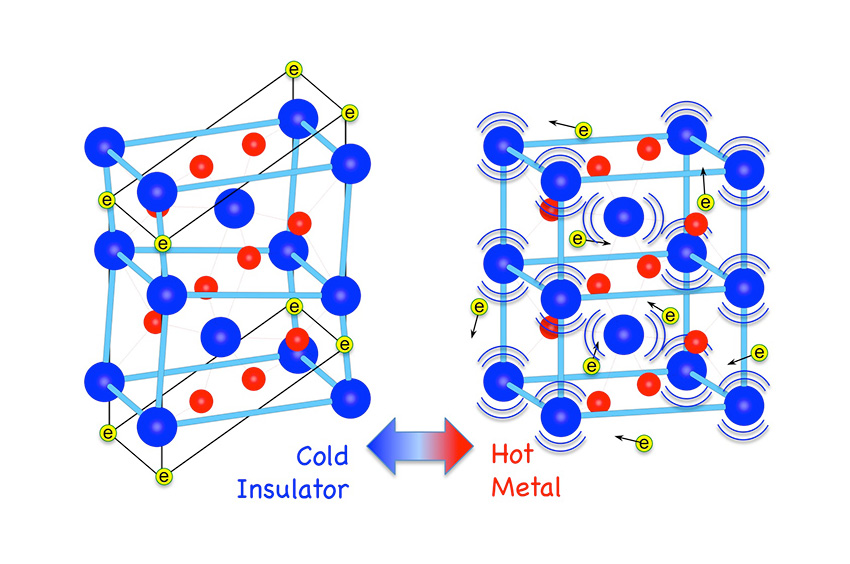
Insulator-to-Metal Transition of Vanadium Dioxide
New studies explain the transition, providing a quantitative picture of a 50-year-old mystery.

New studies explain the transition, providing a quantitative picture of a 50-year-old mystery.
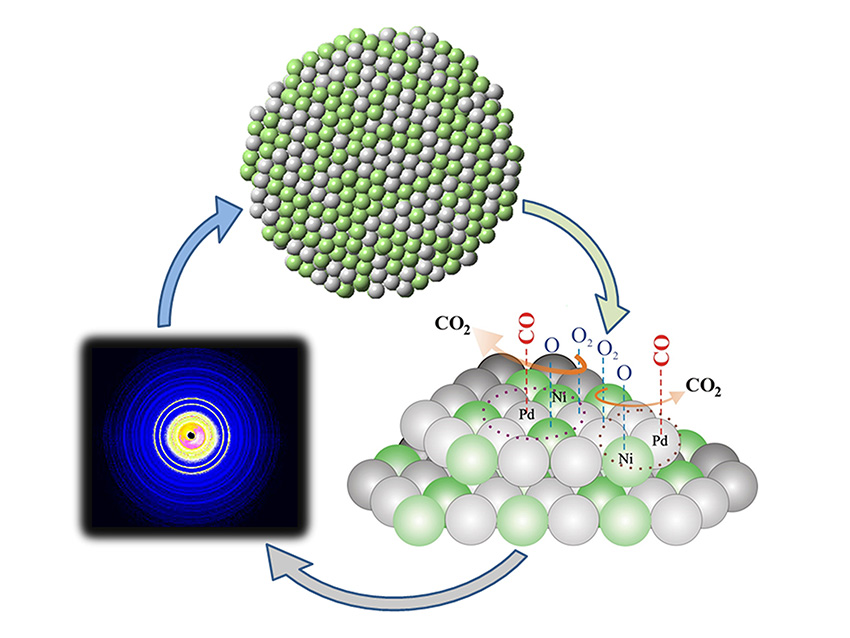
Clusters with longer separations between atoms had enhanced catalytic activity.
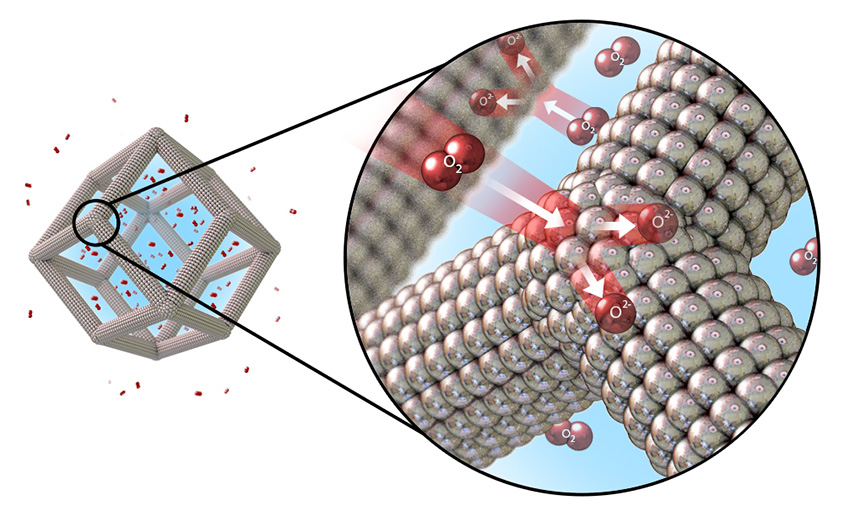
Concentrating noble-metal catalyst atoms on the surface of porous nano-frame alloys shows over thirty-fold increase in performance.
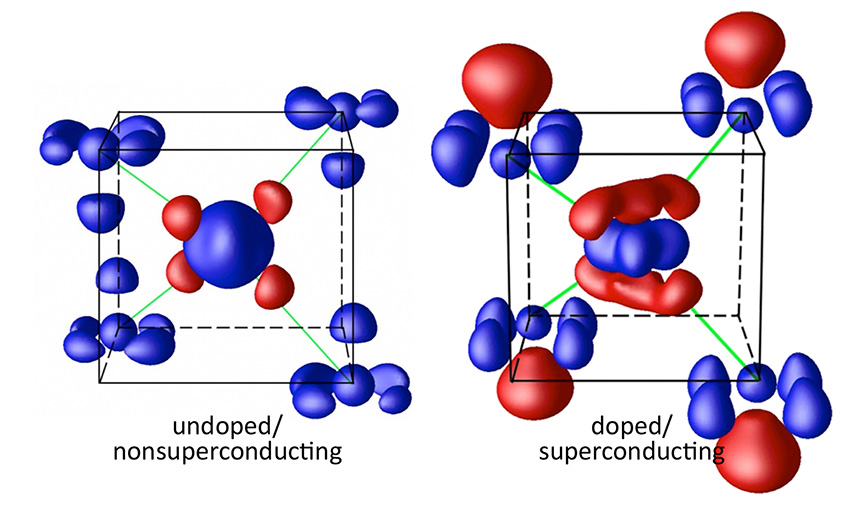
Atomic-scale details of electron distribution reveal a novel mechanism for current to flow without energy loss.
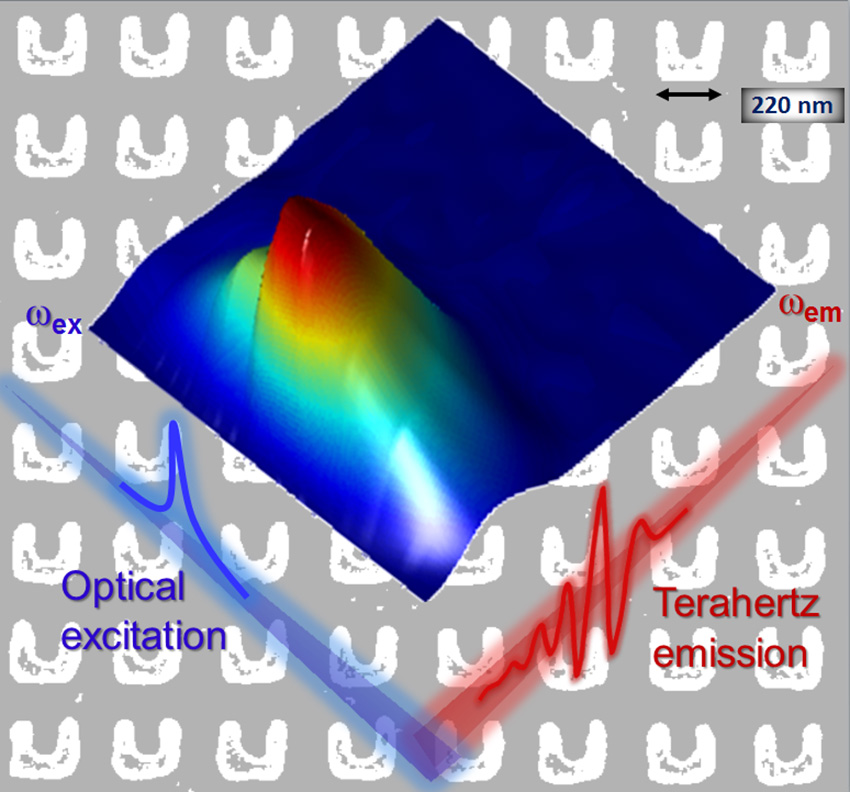
Discovery demonstrates how metamaterials may be used in non-invasive material imaging and sensing, and terahertz information technologies.
![figure-1-large.jpg Crystal structure of the parent compound of a calcium-strontium-based cuprate superconductor [(Ca/Sr)2CuO3]](/-/media/bes/images/highlights/2015/02/figure-1-large.jpg?h=640&w=482&la=en&hash=D1DB4EF52CFDD381CF2E3555D27C4B6F5EB9C292E8C55E49392F2B5AA679B0B5)
New theoretical techniques predict experimental observations in superconducting materials.
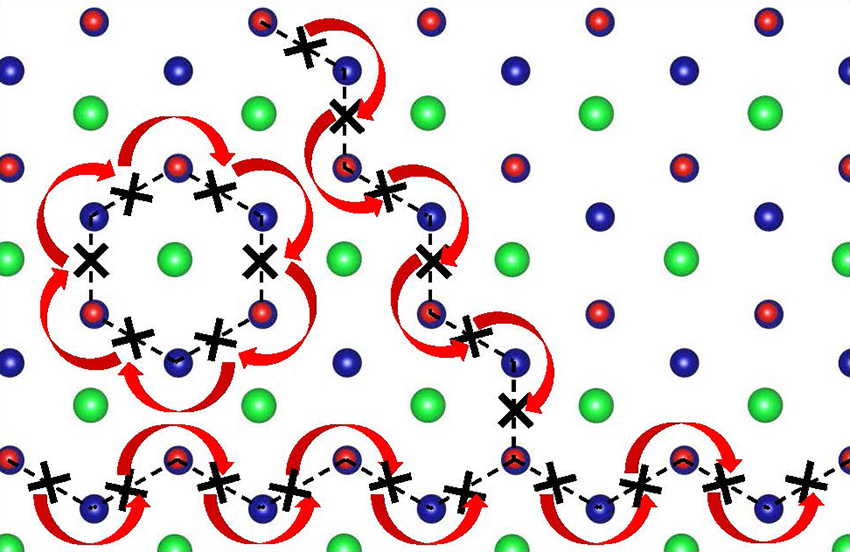
New metal oxide material works at temperatures low enough to improve fuel cell efficiency.
Coexistence of two states of matter that normally avoid one another is revealed by inelastic neutron scattering experiments.
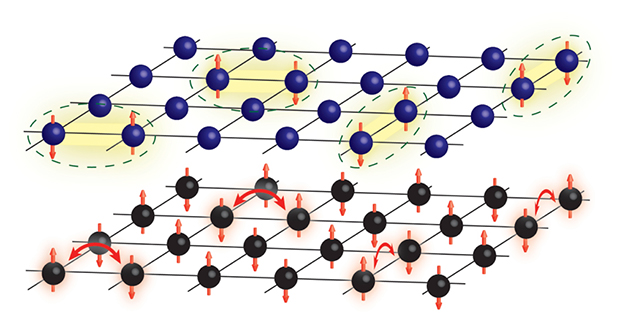
Microscopic understanding offers fresh directions for discovering new materials to transmit energy without loss.
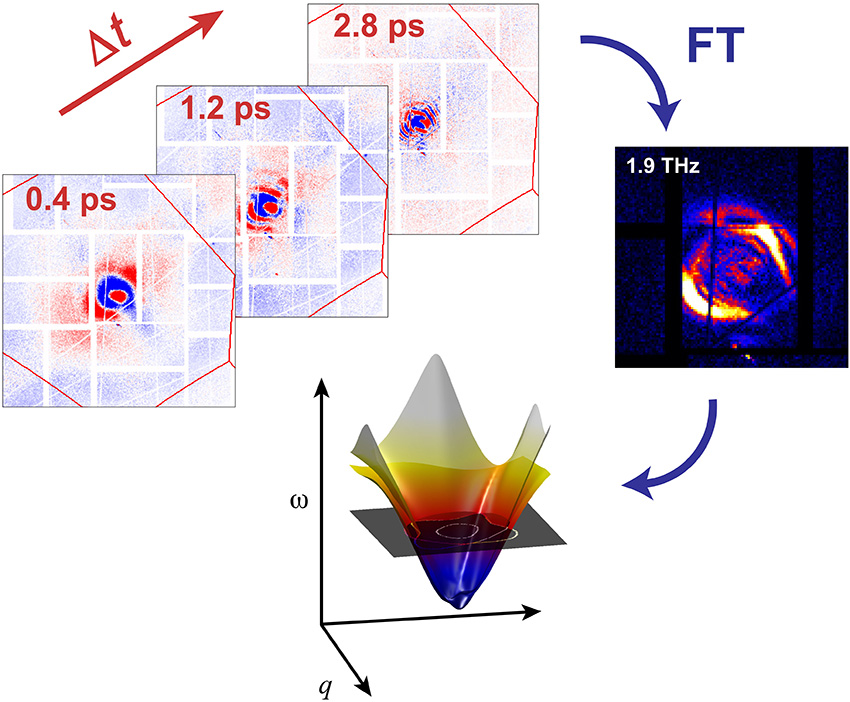
Stroboscopic x-ray pulses scatter from a vibrating crystal and reveal how energy moves.

Method enables quantification of thiols on bacteria and natural organic matter.
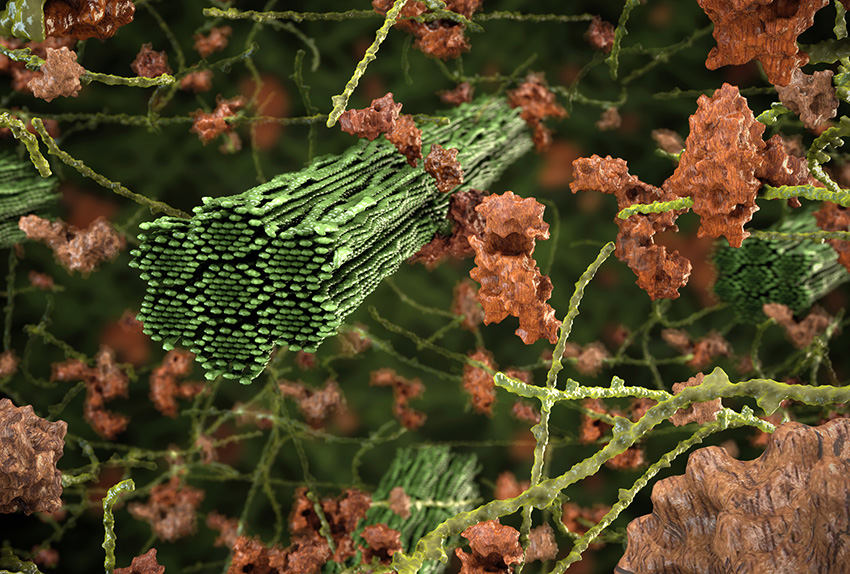
Study reveals insights into plant structural changes during bioenergy pretreatments.