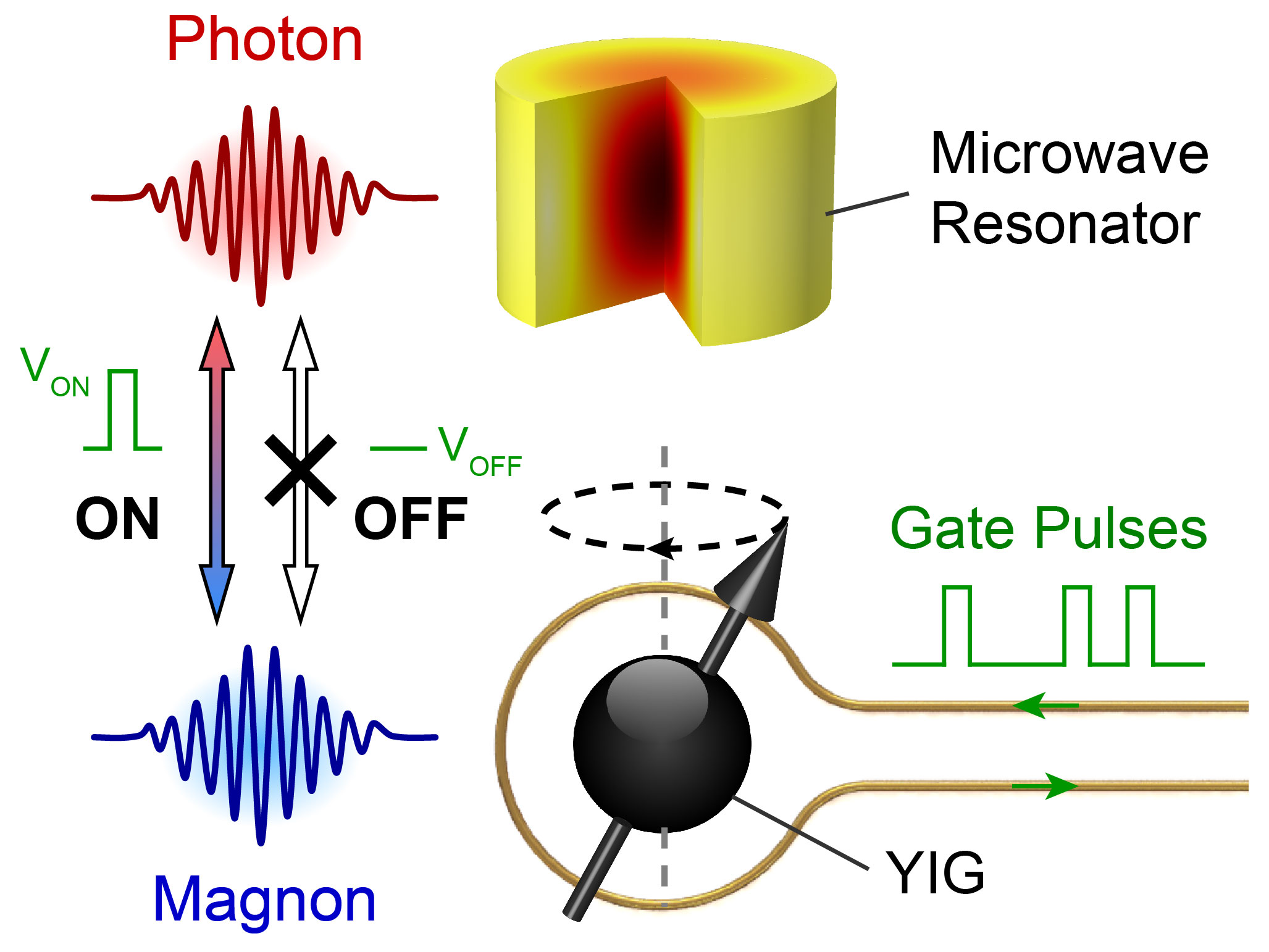
Opening the Door to a Next-Generation Information Processing Platform
New gate design leads to fast coherent control of novel electromagnonics devices.

New gate design leads to fast coherent control of novel electromagnonics devices.
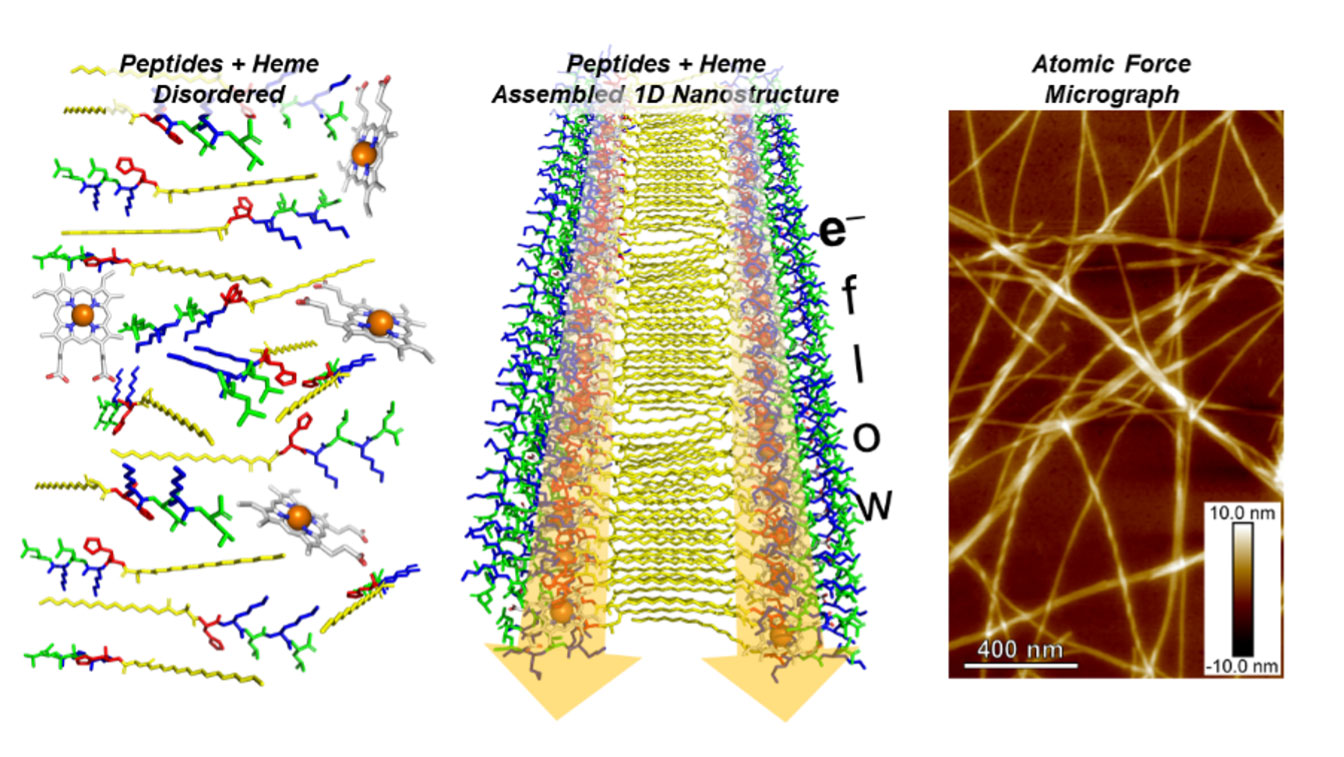
Synthetic peptide assemblies show promise as bioelectronic materials.
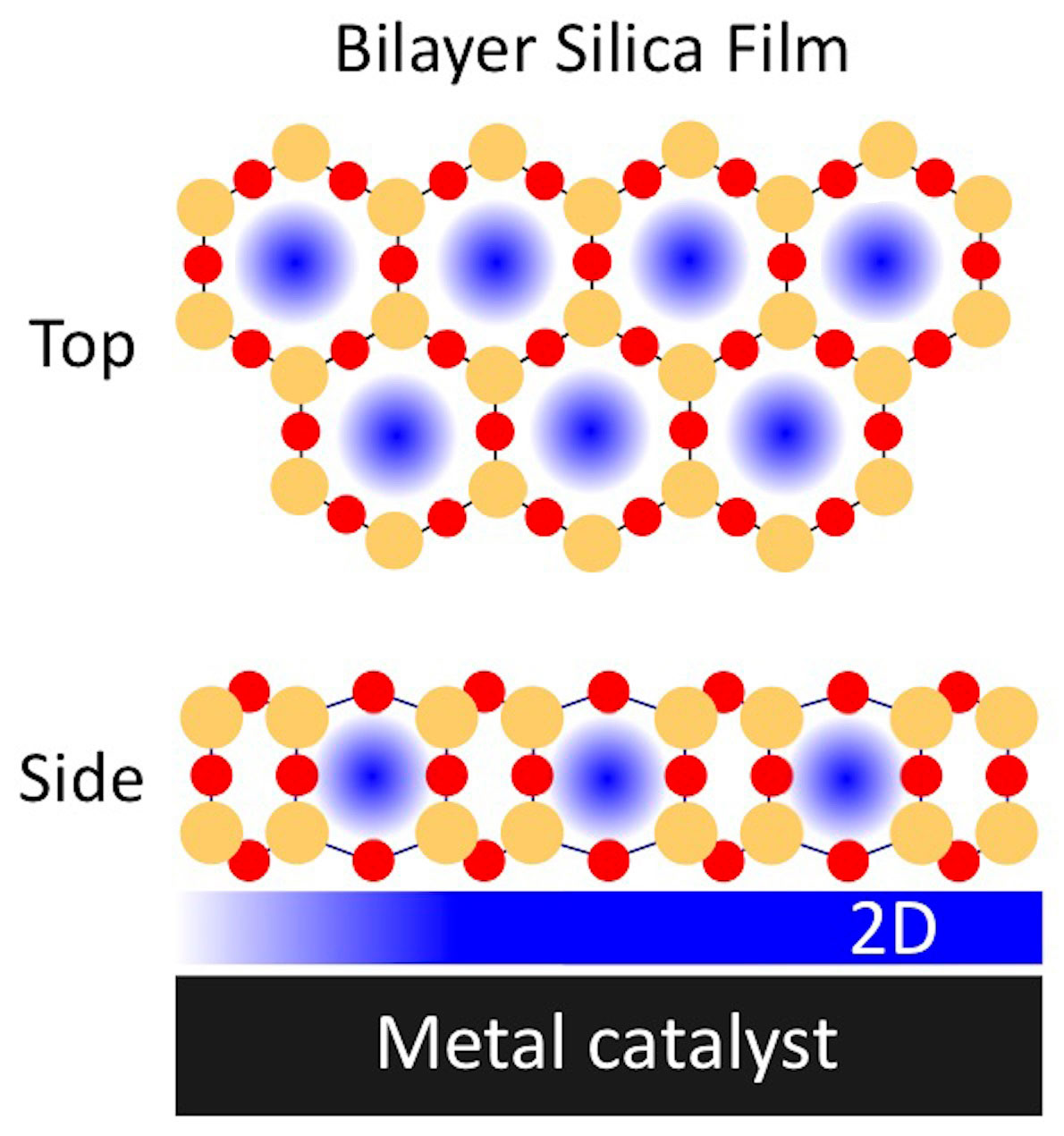
Covering metal catalyst surfaces with thin layers of oxide materials can enhance chemical reactions.
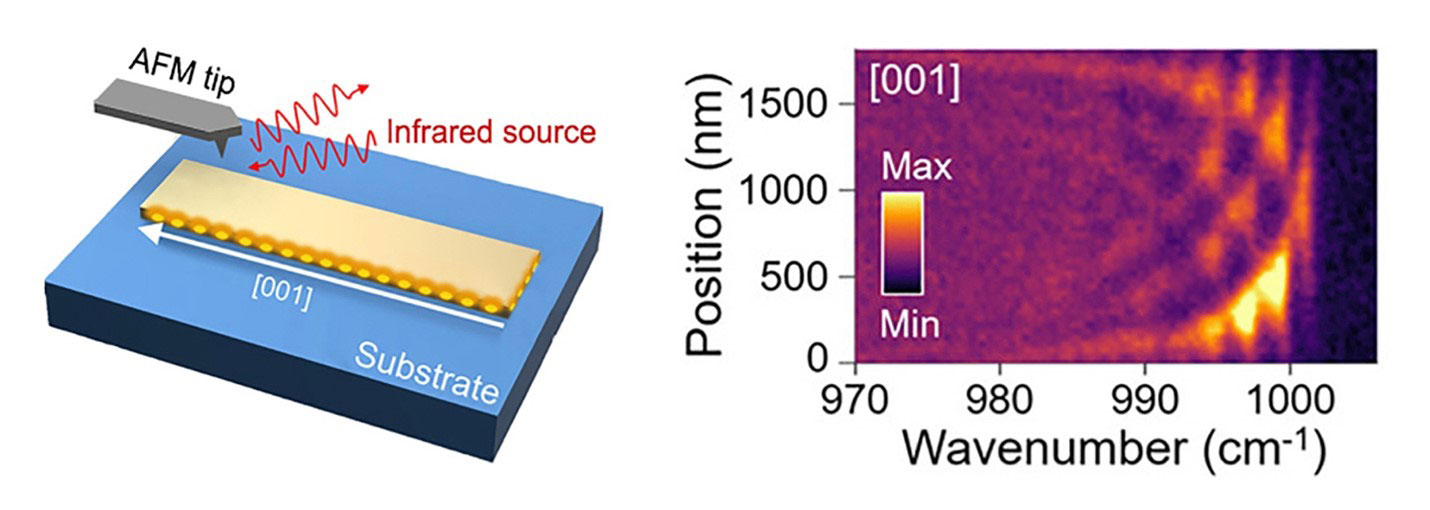
Crystalline nanoribbons synthesized to resonate with infrared light for imaging, sensing, and signaling pass a crucial test.
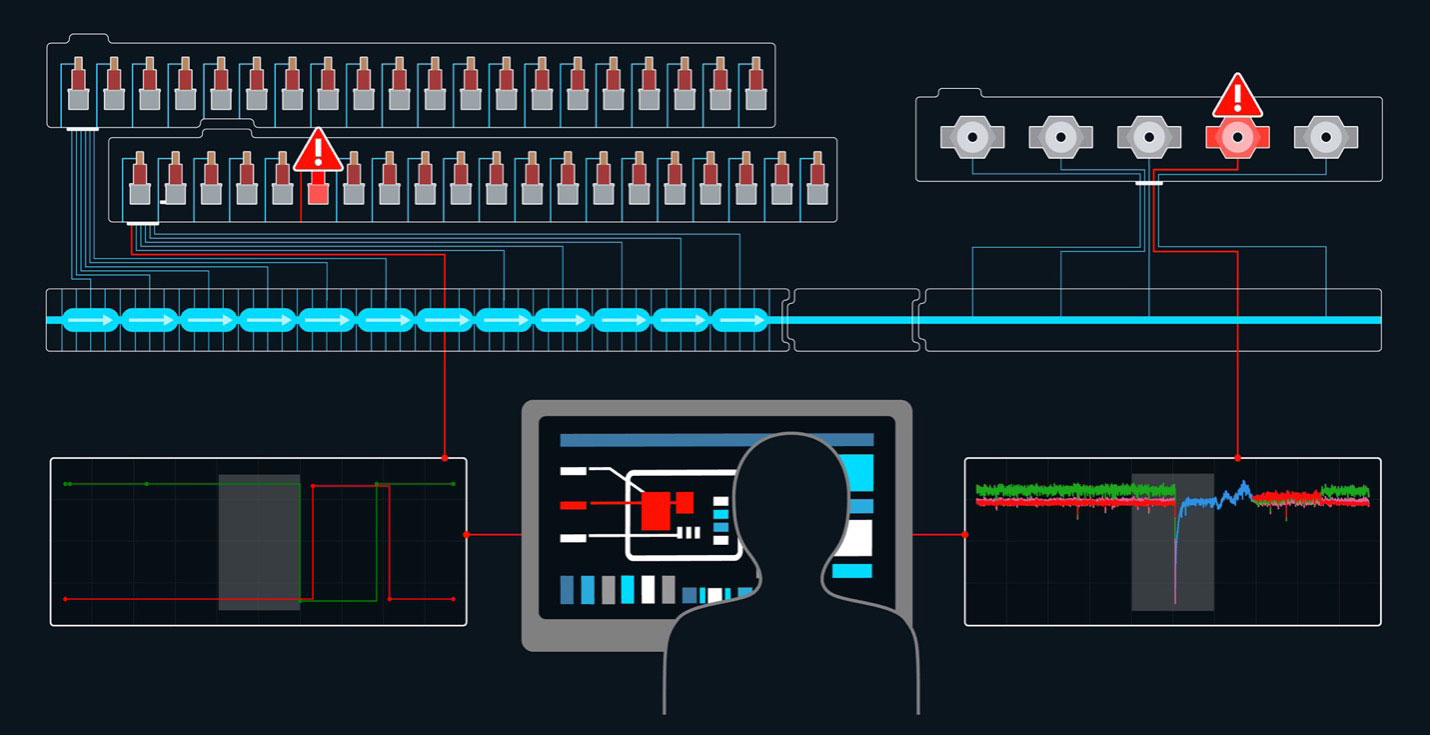
Machine learning methods support human operators in diagnosing and fixing failing subsystems in an accelerator-driven X-ray laser.
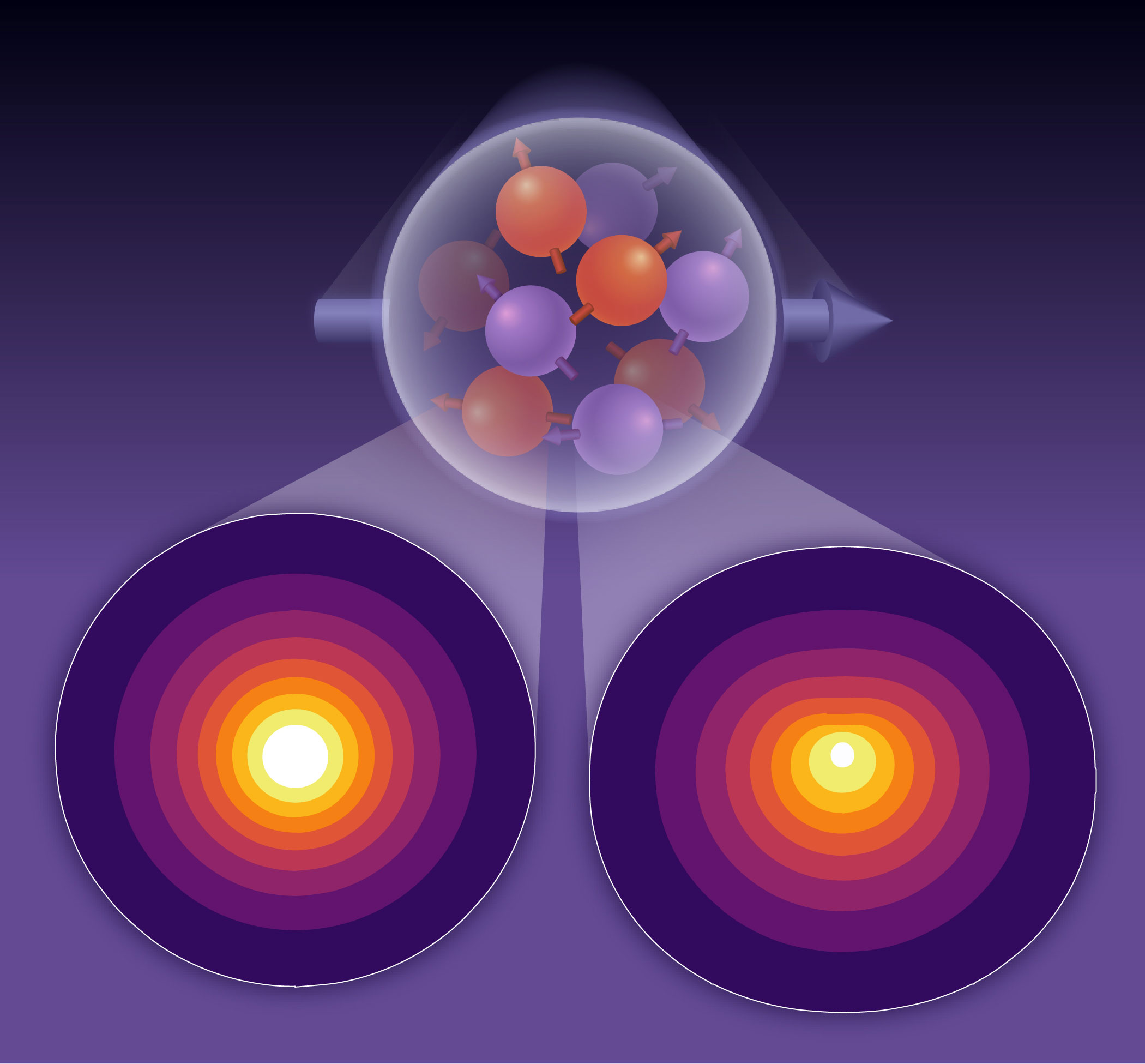
Theorists predict differential distribution of 'up' and 'down' quarks within protons—and differential contributions to the proton's properties.
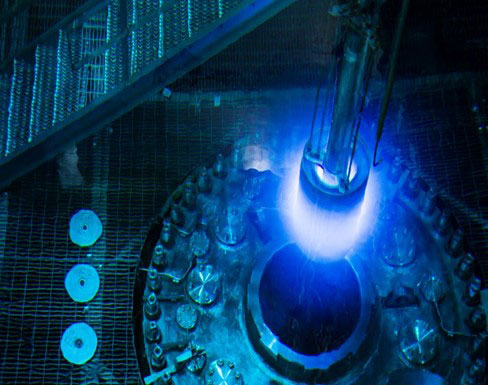
Experiment at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s High Flux Isotope Reactor precisely measures the antineutrino energy spectrum.
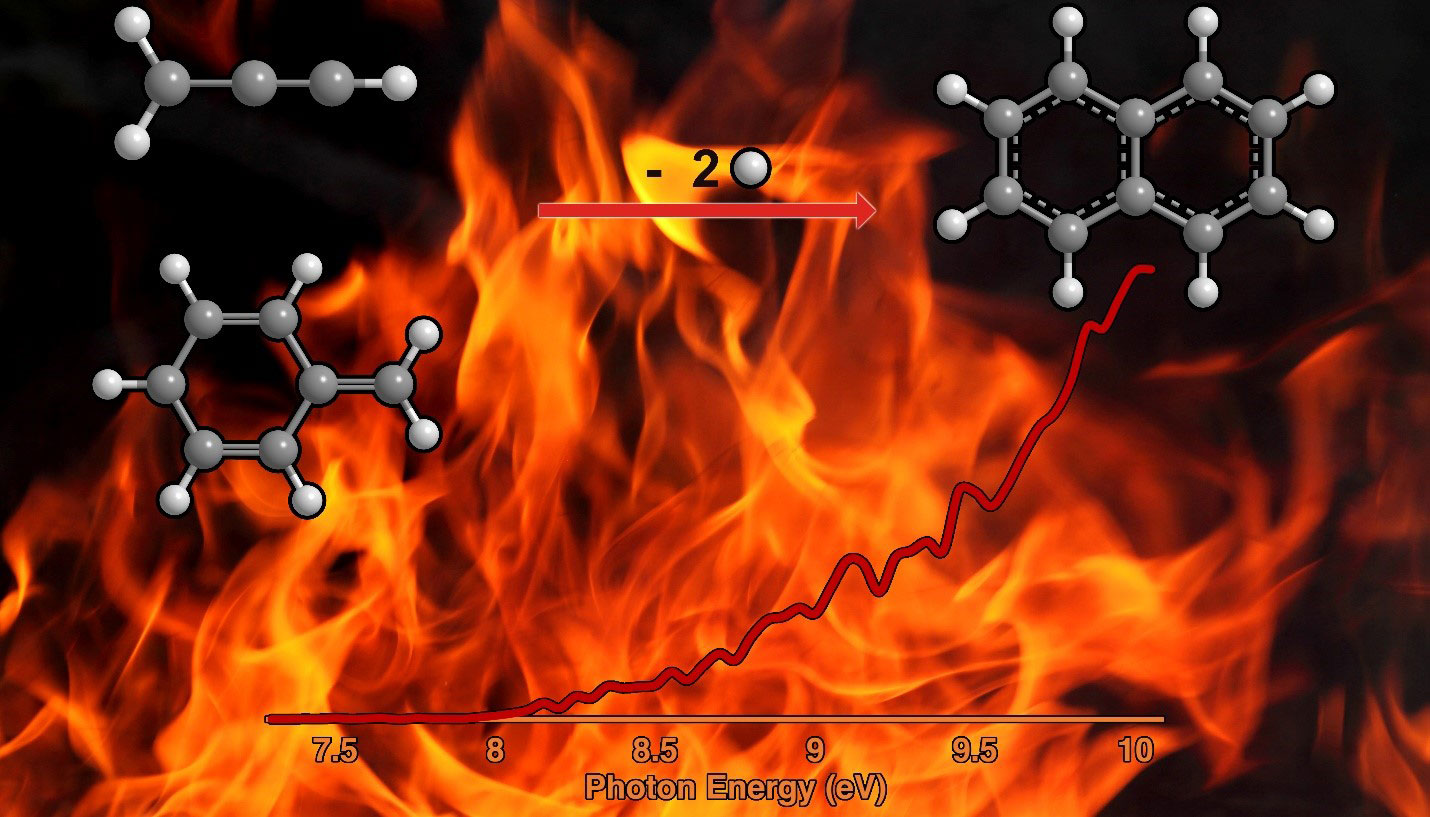
A molecule found in combustion on Earth and surrounding some stars can lead to the formation of an important organic hydrocarbon.
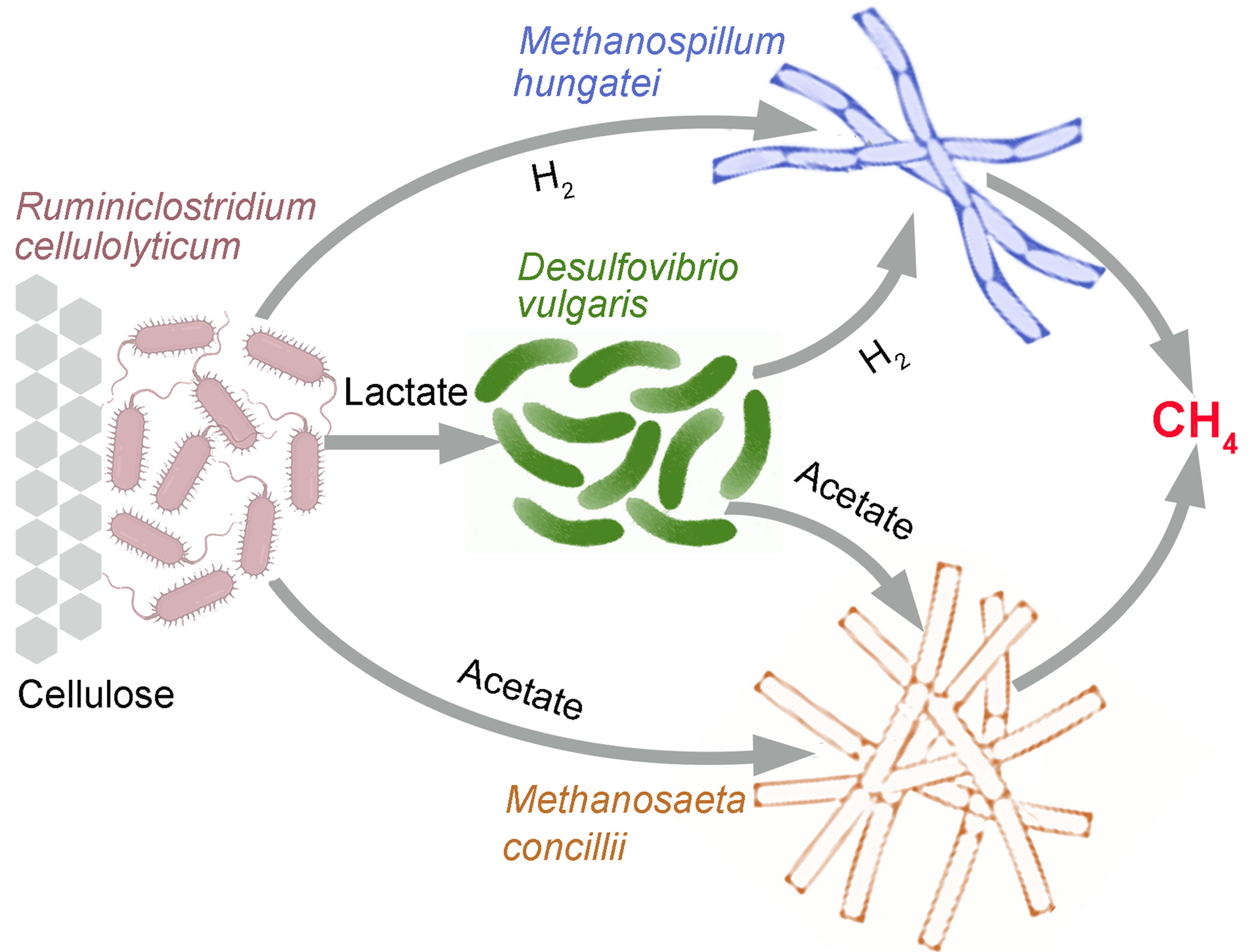
Modeling microbial interactions in synthetic communities offers insights into environmental processes.

A unique study of a key reaction in X-ray burst nucleosynthesis bolsters the theoretical models used to calculate reaction rates.
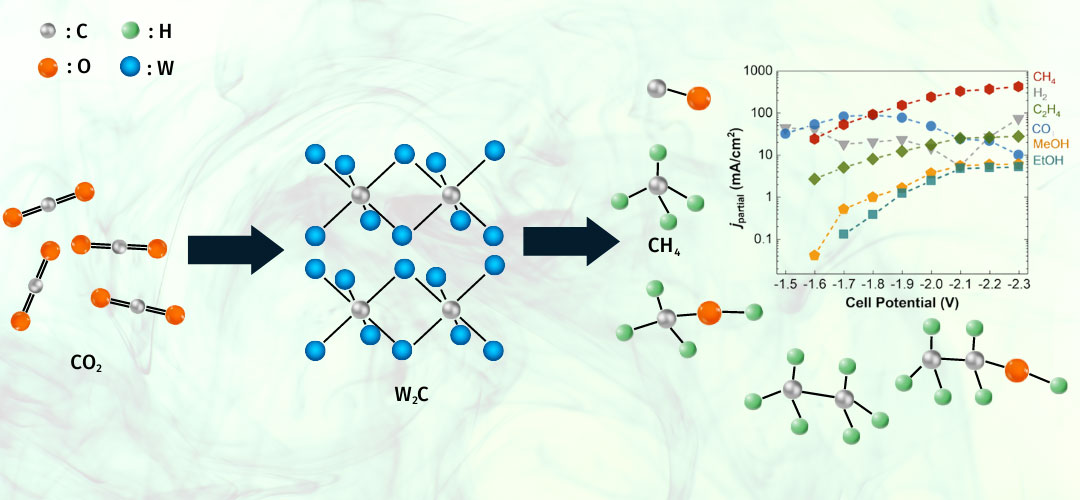
A tungsten carbide catalyst can produce a hydrocarbon from carbon dioxide at high rates and high efficiency.
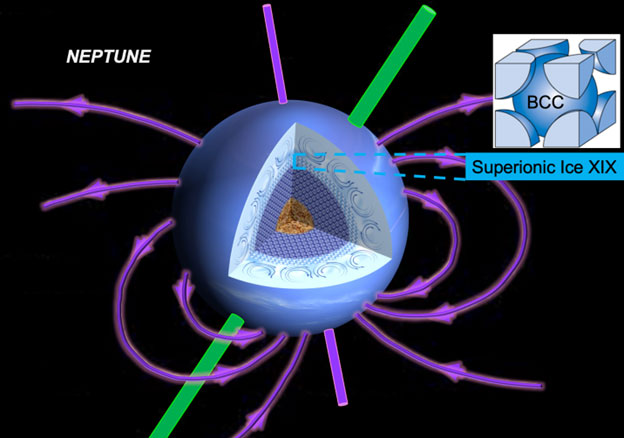
Ultrafast X-ray studies reveal the existence of Superionic Ice XIX, which could explain the unusual magnetic fields of icy giant planets.