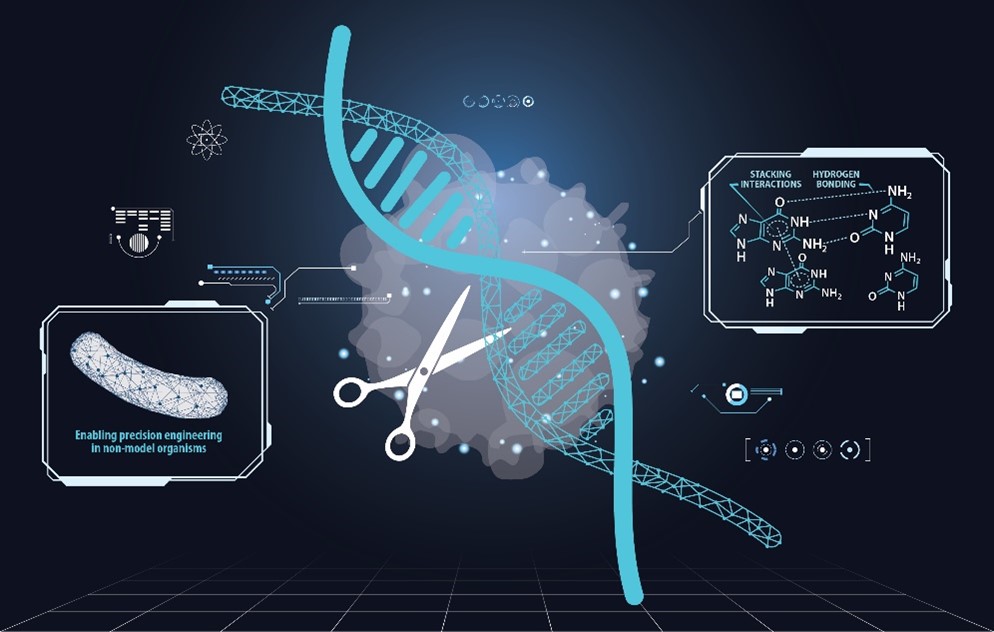
How the Quantum World Can Help Scientists Engineer Biology
Improving genome engineering with quantum biology and artificial intelligence.

Improving genome engineering with quantum biology and artificial intelligence.
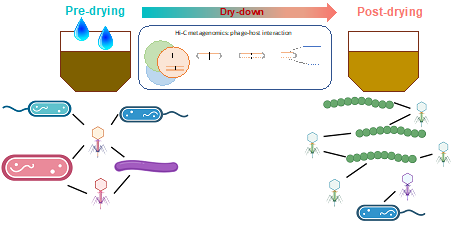
The first application of High-Throughput Chromosome Conformation Capture (Hi-C) Metagenome Sequencing to soil captures phage-host interactions at the time of sampling.
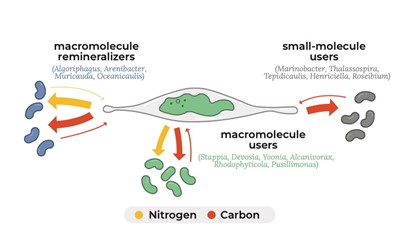
High resolution isotope analysis of the algal microbiome identifies ecological strategies not predicted by genome content.
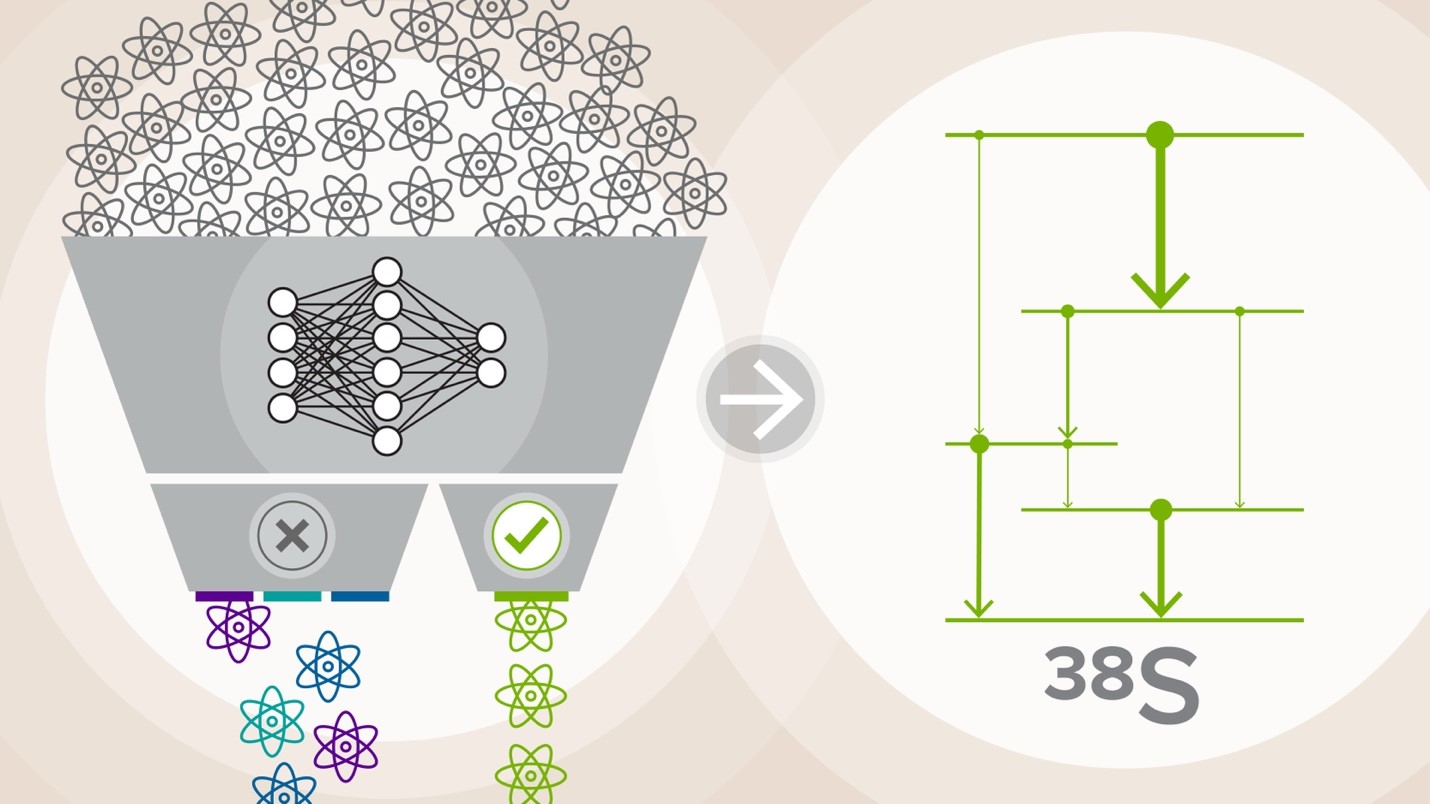
Forefront nuclear physics capabilities and machine-learning data analyses combine to generate new information on quantum energy levels in sulfur-38.
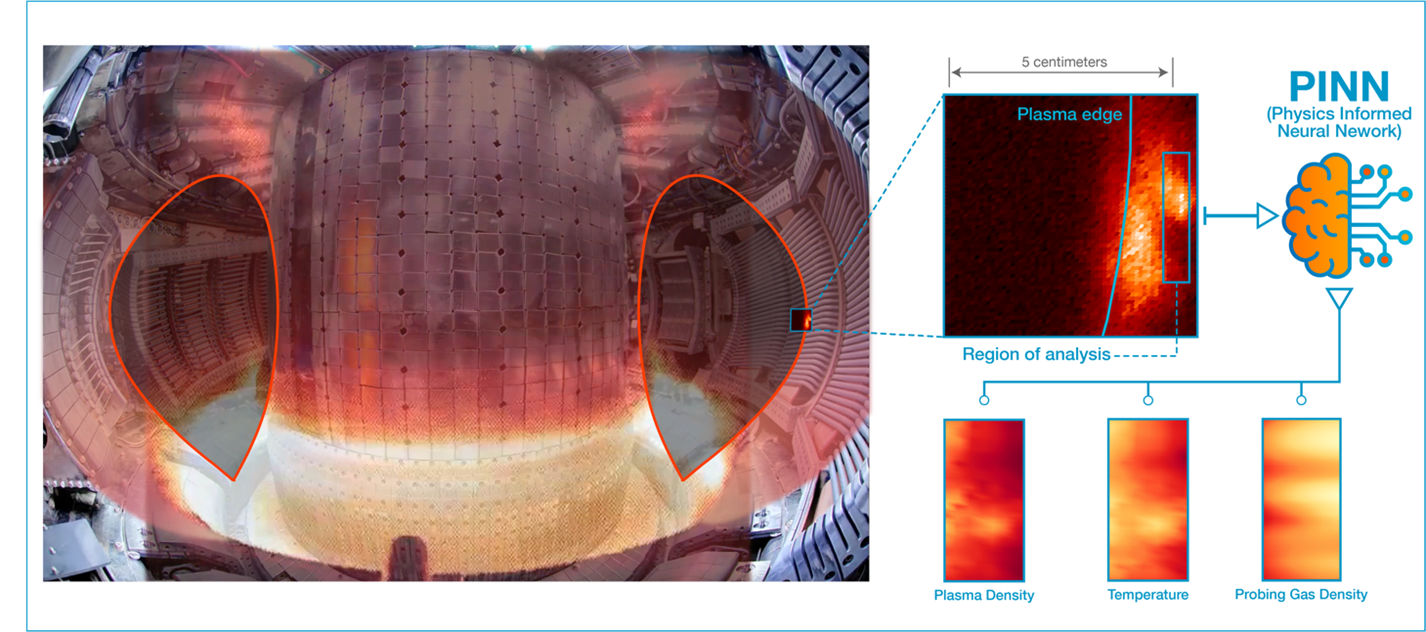
Neural networks guided by physics are creating new ways to observe the complexities of plasmas.
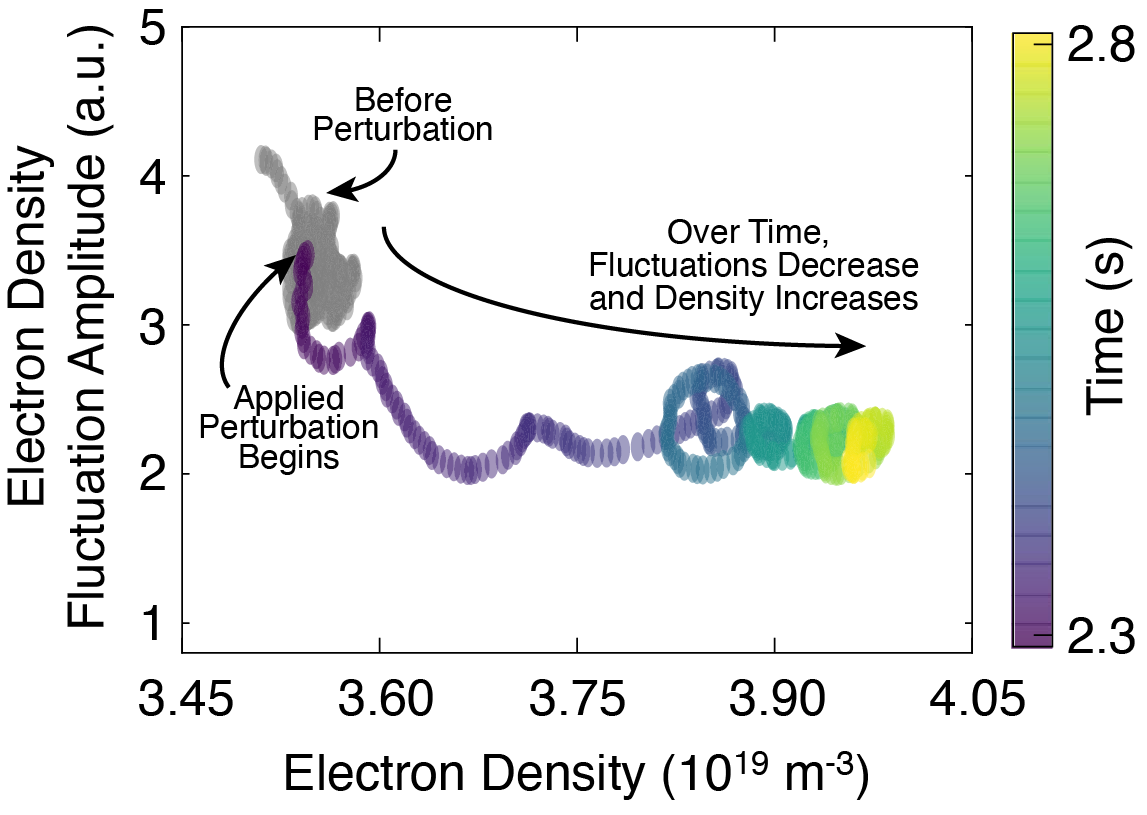
Perturbing the edge magnetic field of a tokamak produces a counterintuitive response: particles entering the confined region rather than escaping it.
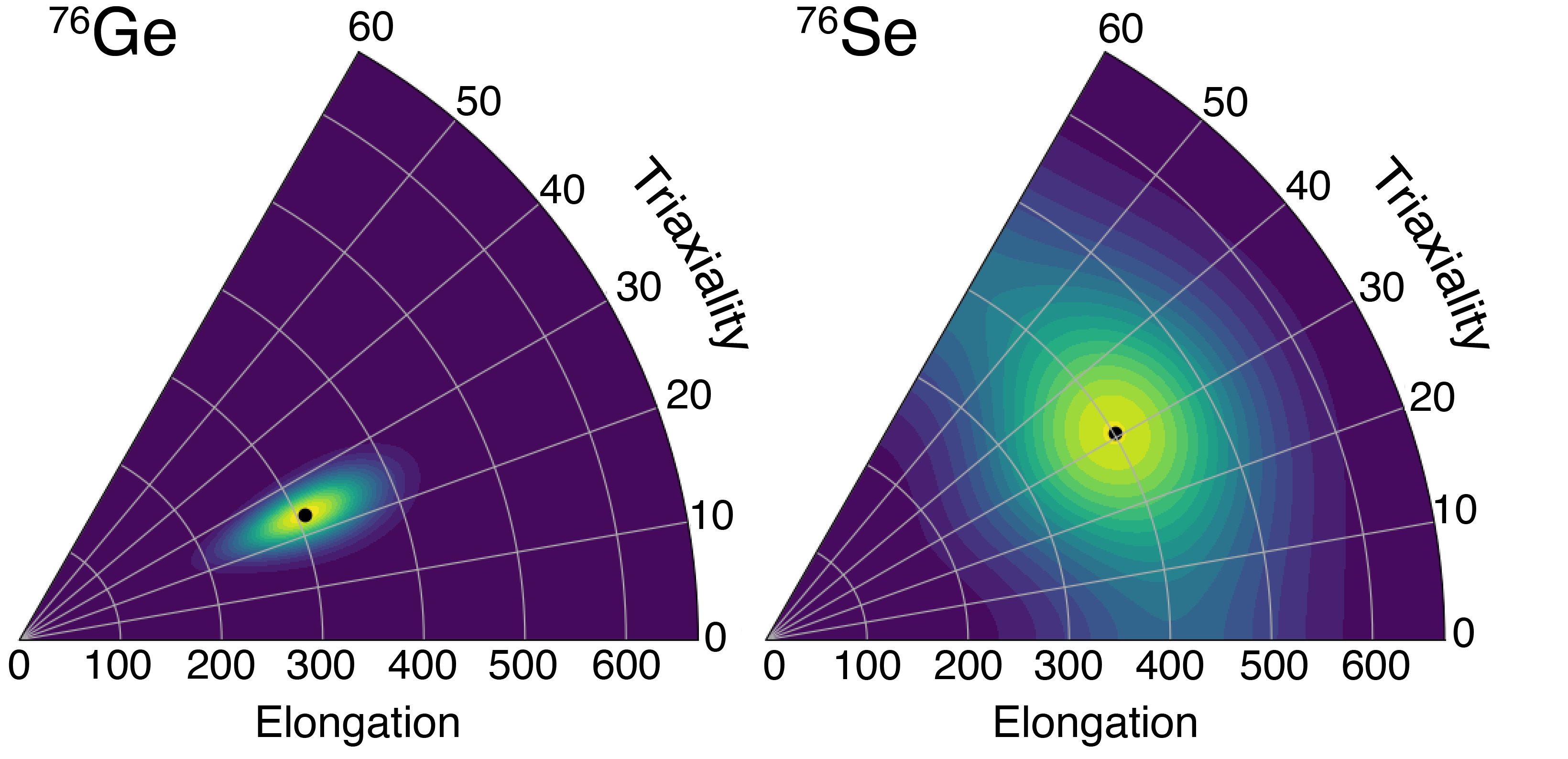
Scientists investigate neutrinoless double beta decay through neutrino mass and the nuclear structure of germanium-76.
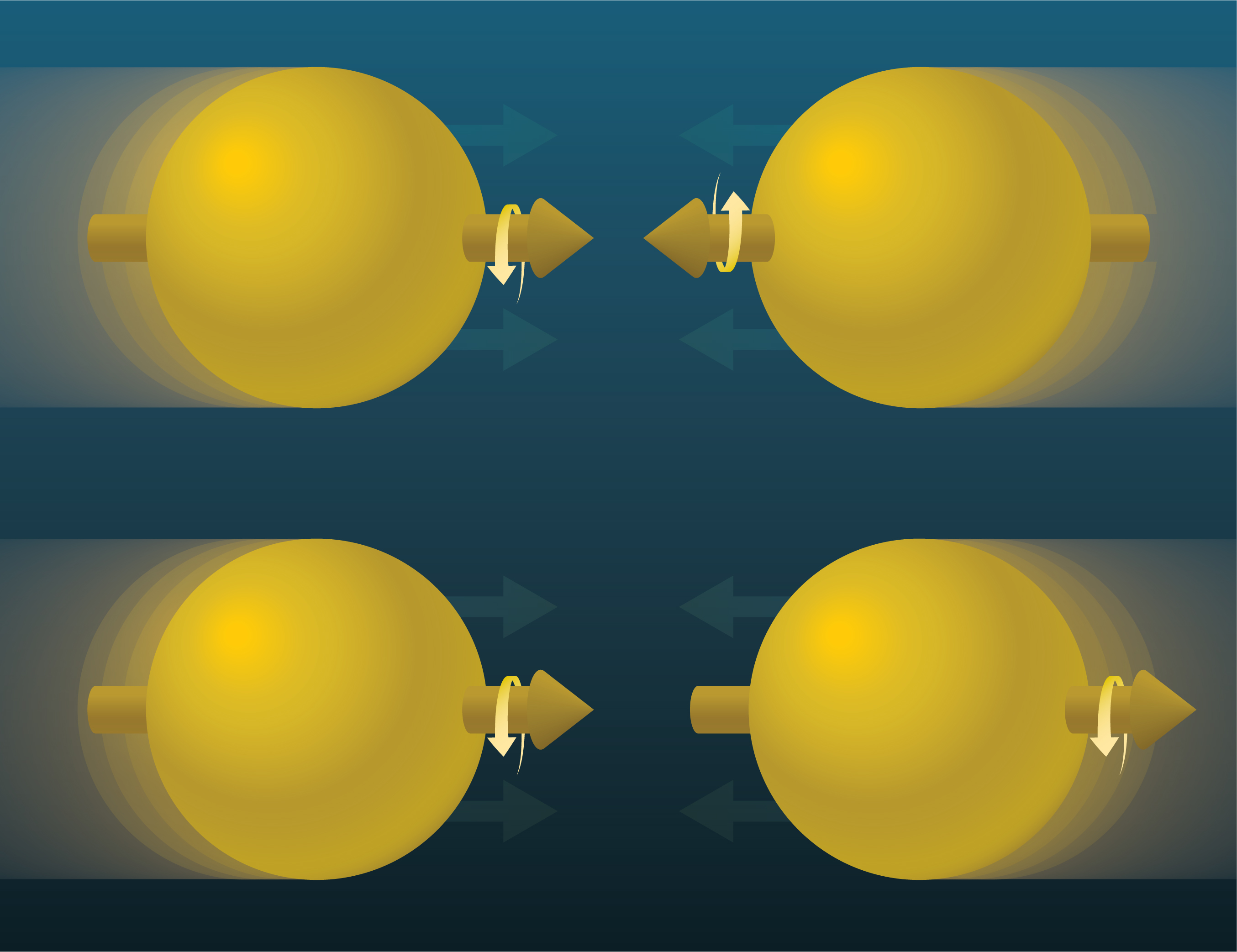
A measurement tracking ‘direct’ photons from polarized proton collisions points to positive gluon polarization.
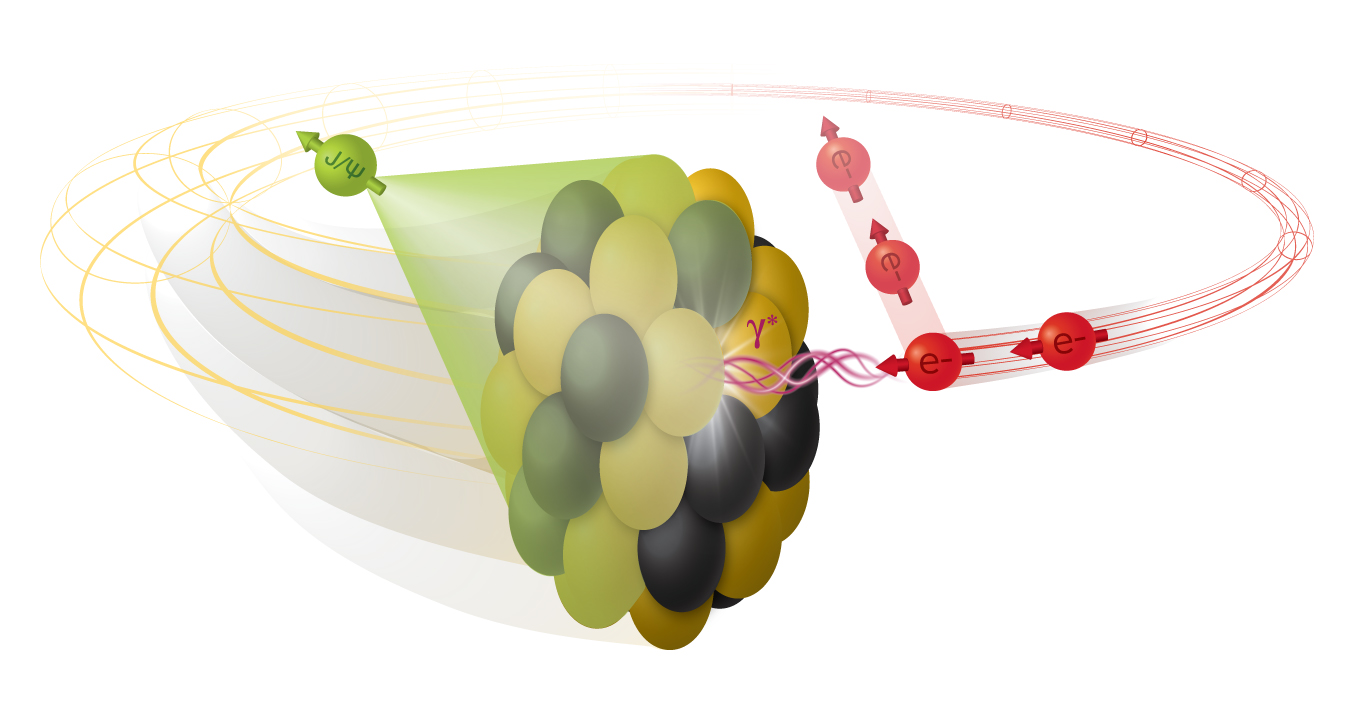
New theoretical work indicates that the future Electron Ion Collider can be used to measure the shape of atomic nuclei.
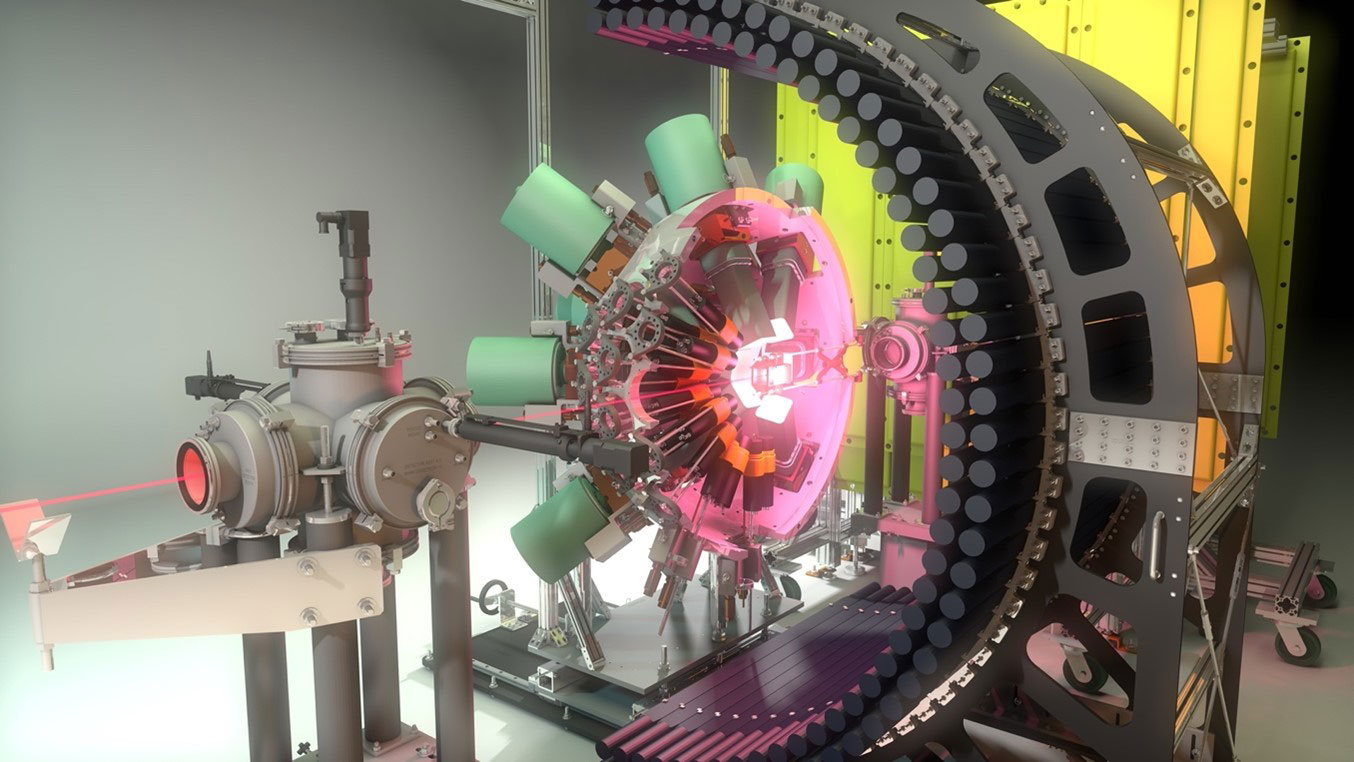
A newly discovered excited state in radioactive sodium-32 has an unusually long lifetime, and its shape dynamics could be the cause.
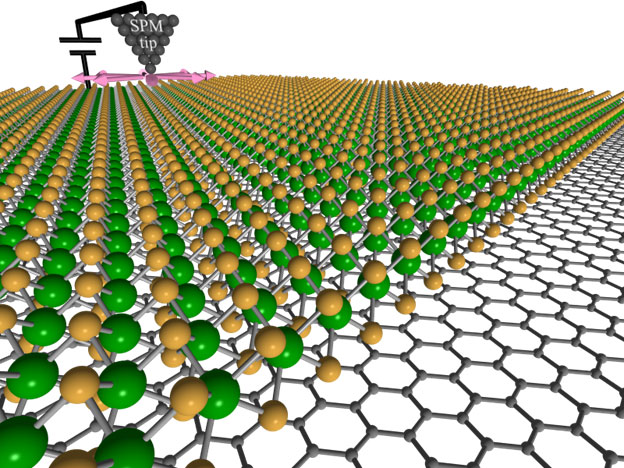
Machine learning and artificial intelligence accelerate nanomaterials investigations.
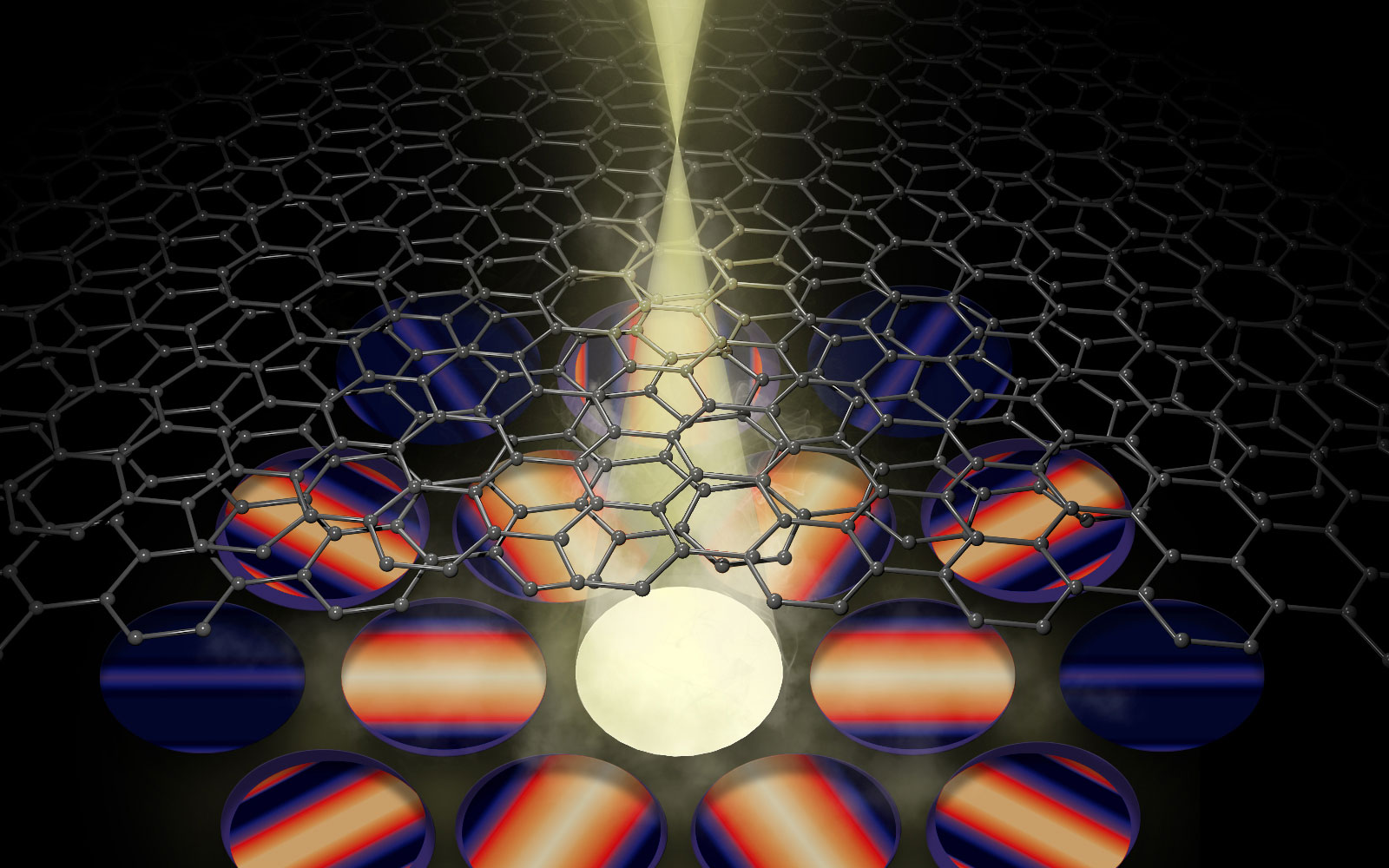
A new microscopy technique measures atomic-level distortions, twist angles, and interlayer spacing in graphene.