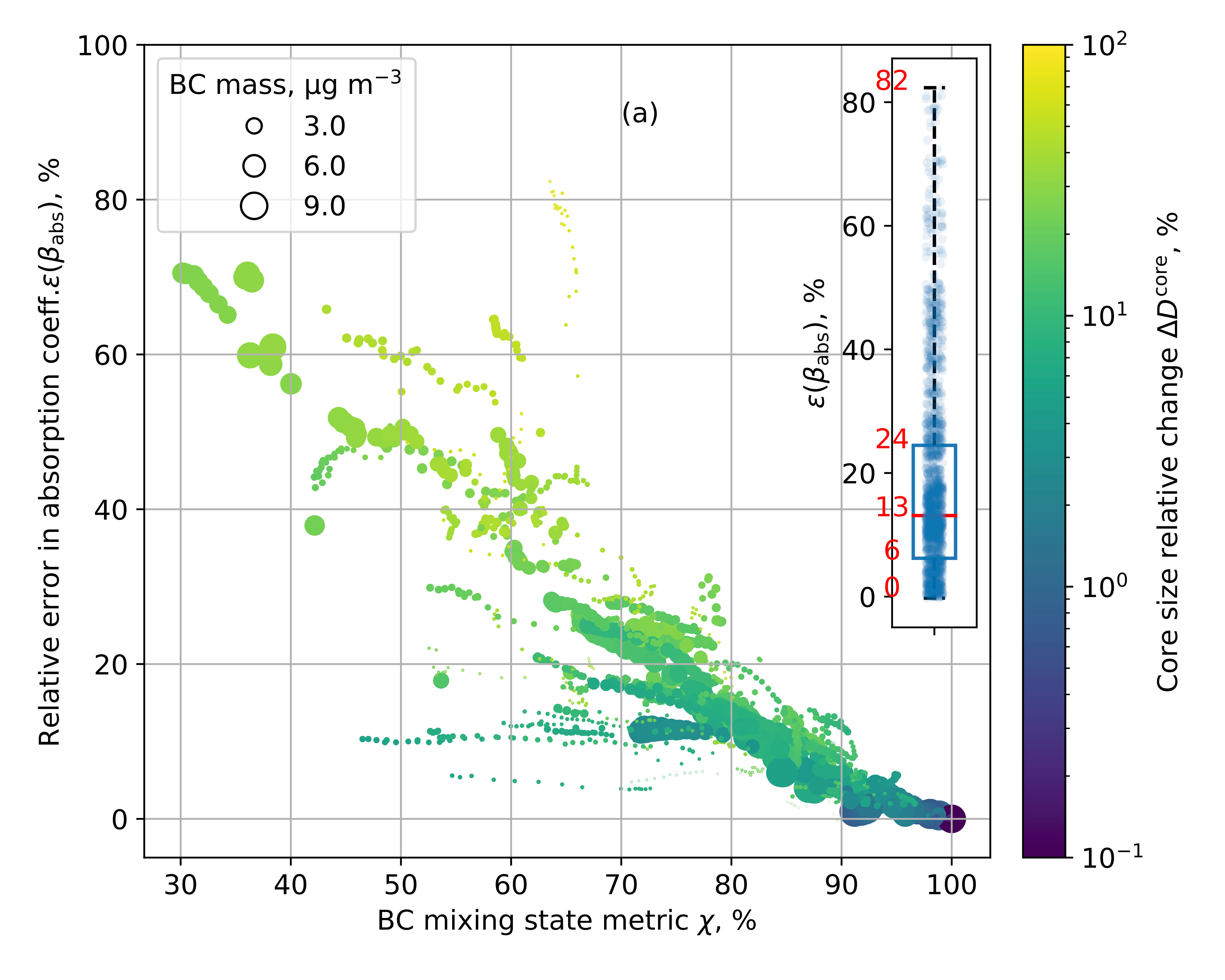
Particle Errors: Quantifying the Effects of Simulation Mixing State on Aerosol Optical Properties
Researchers use particle-resolved model simulations to quantify errors in simulations’ simplified optical properties.

Researchers use particle-resolved model simulations to quantify errors in simulations’ simplified optical properties.
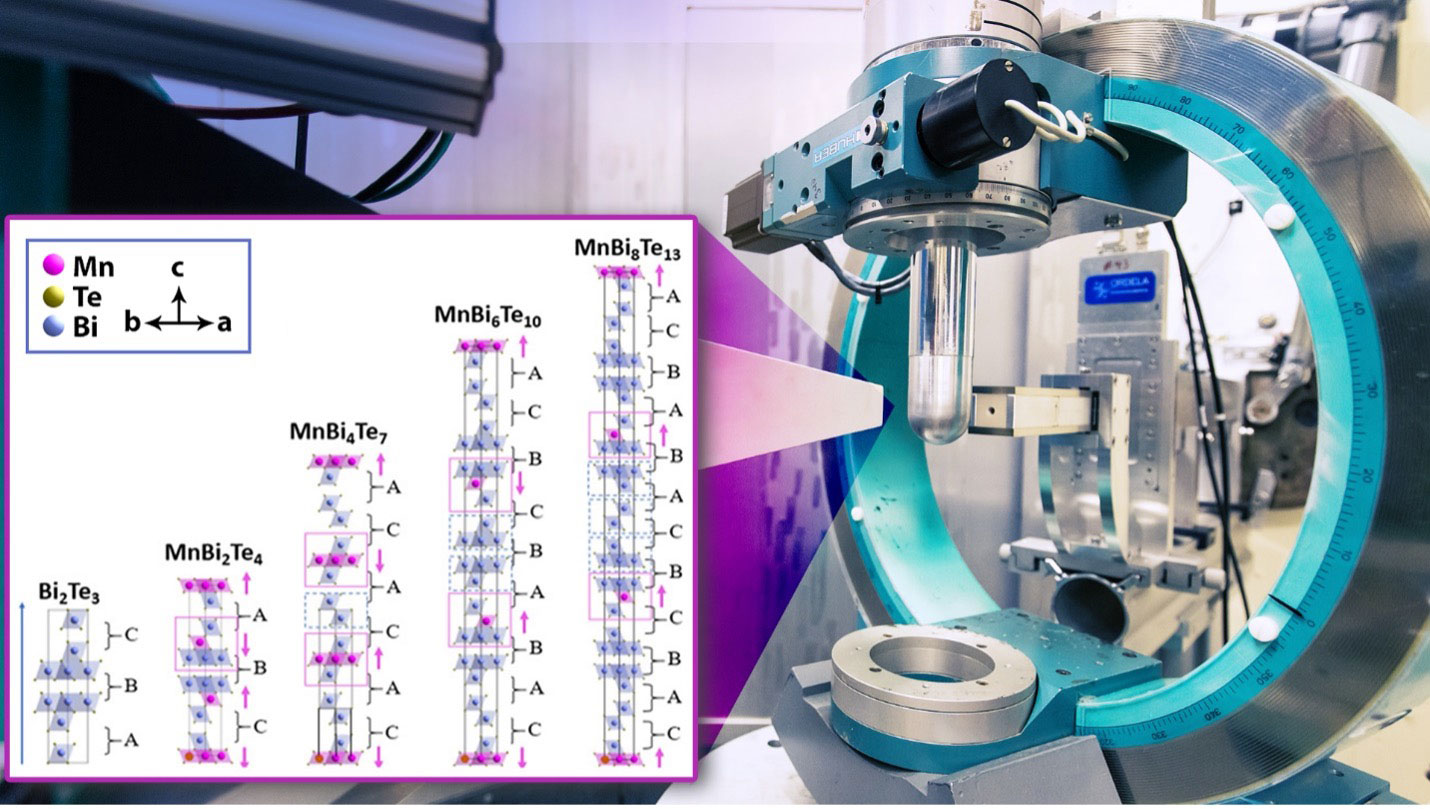

Combining synthesis, characterization, and theory confirmed the exotic properties and structure of a new intrinsic ferromagnetic topological material.
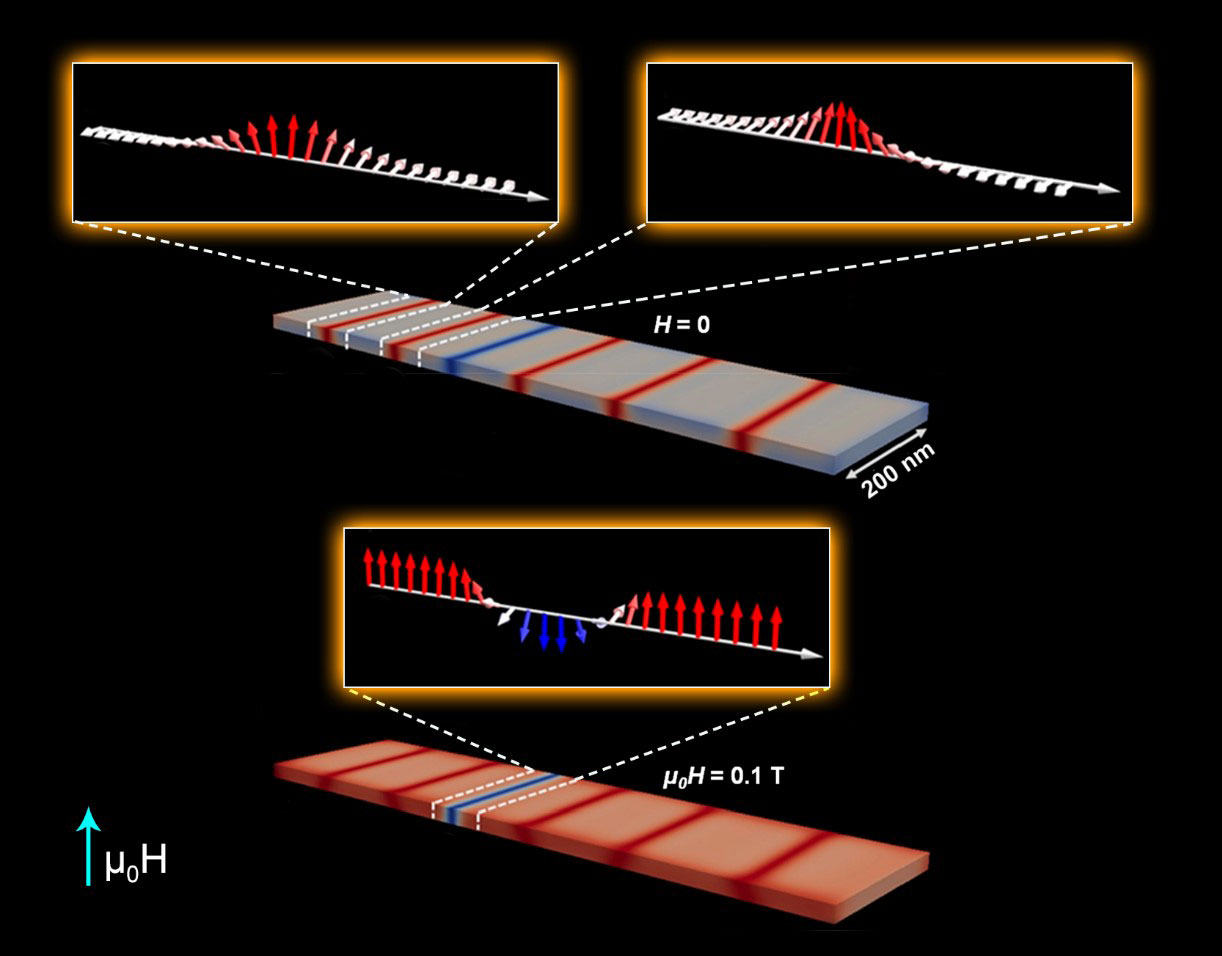
Studies of the nanostructure of a chiral magnet provides insights on controlling magnetic properties for applications in computers and other electronics.

Short and long-range electron transfer compete to determine free-charge yield in organic semiconductors.

Researchers discover key details of how to drive photosynthesis in the shade by studying far-red light acclimation in cyanobacteria.
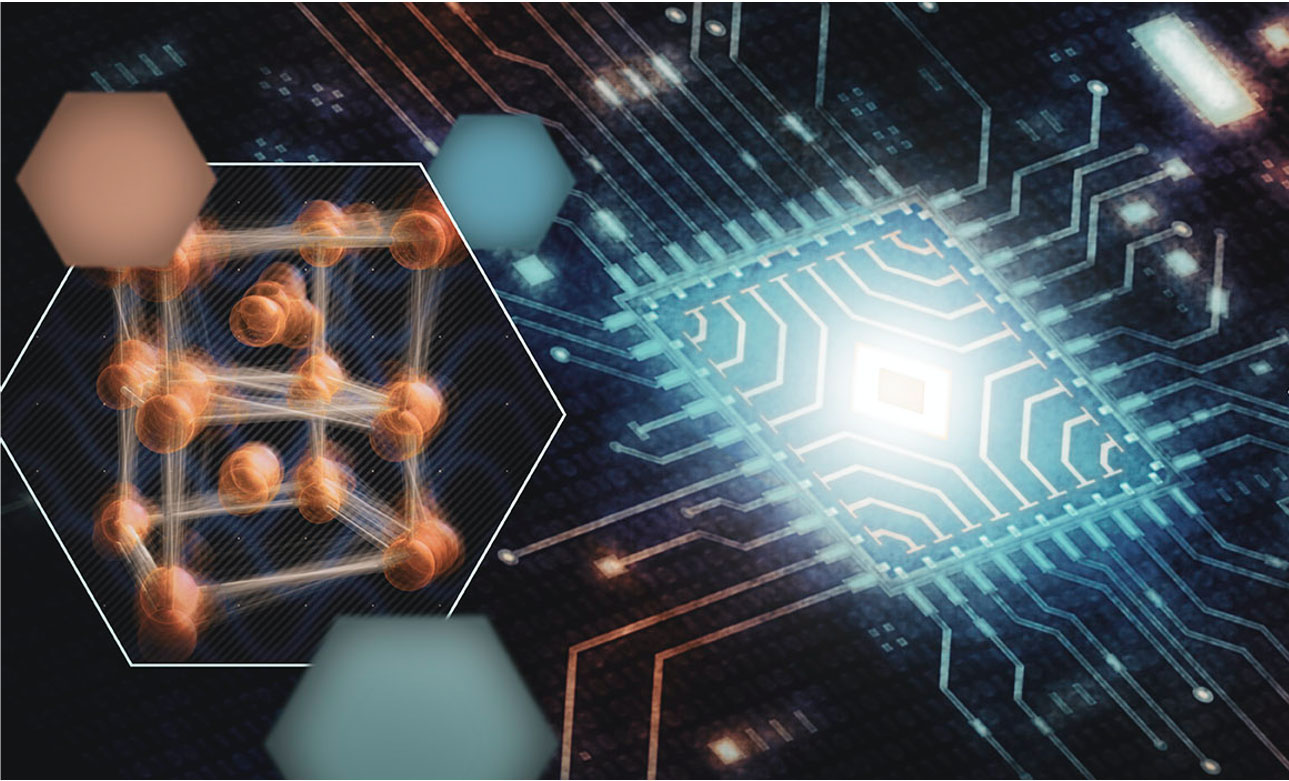

Discovery of a short-lived state could lead to faster and more energy-efficient computing devices.
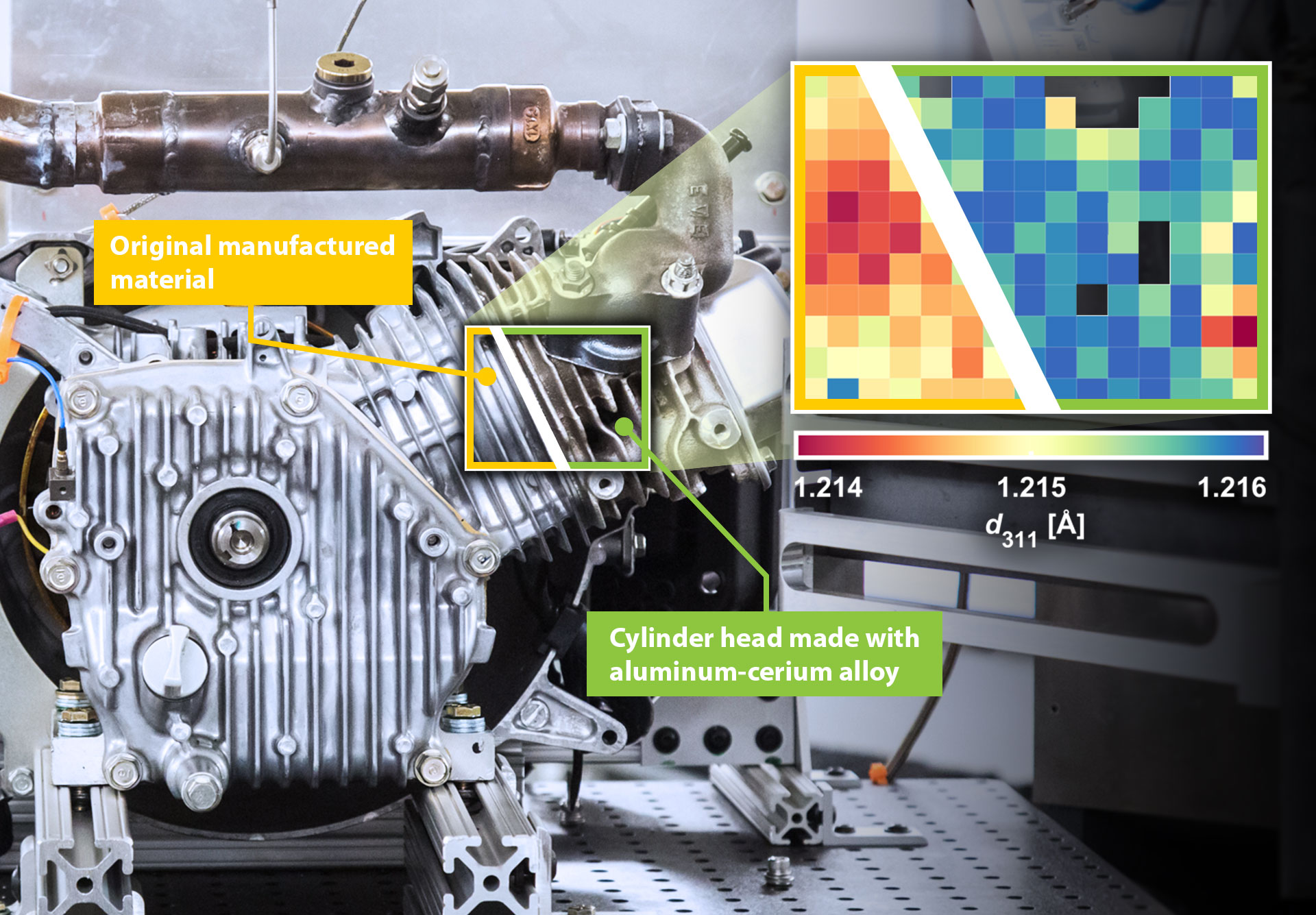
Scientists map atomic-level changes in the components of a running internal combustion engine using neutron techniques.
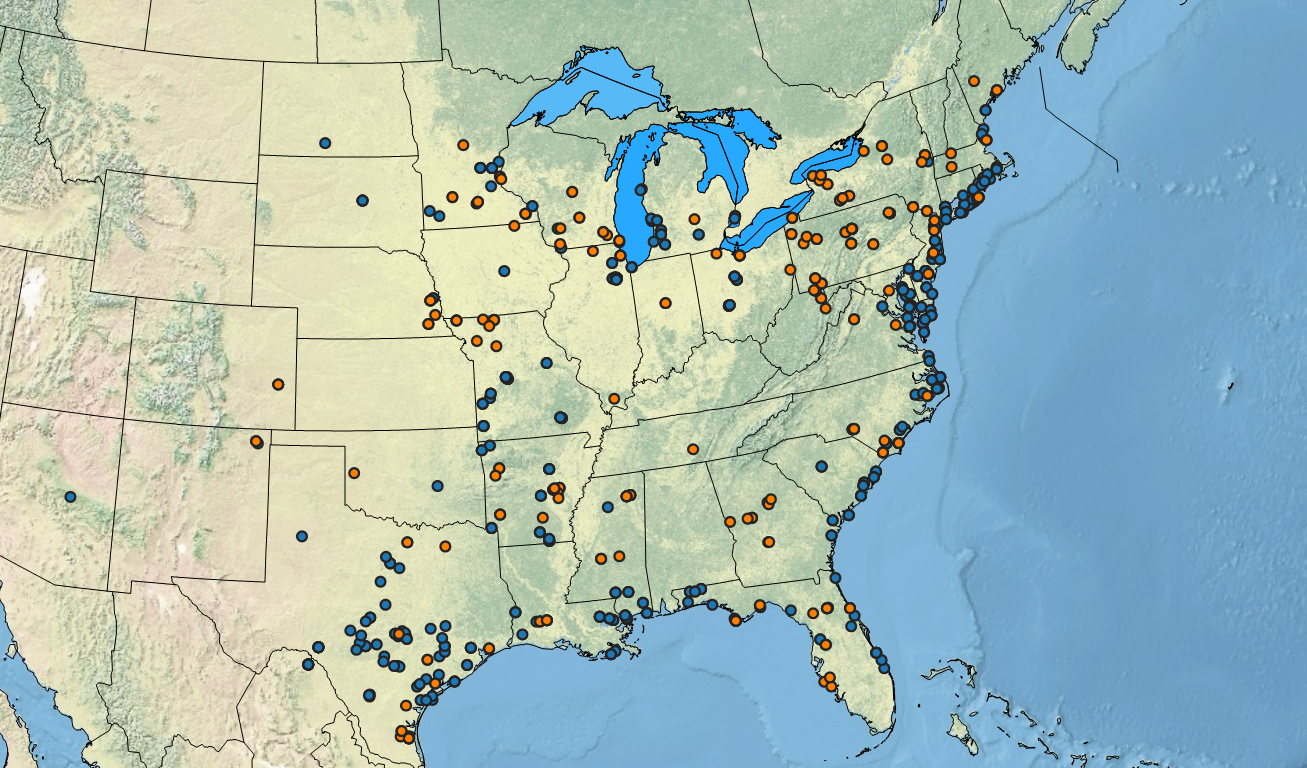
Varieties of switchgrass with different numbers of genome copies use different strategies in adapting to changes in climate and location.
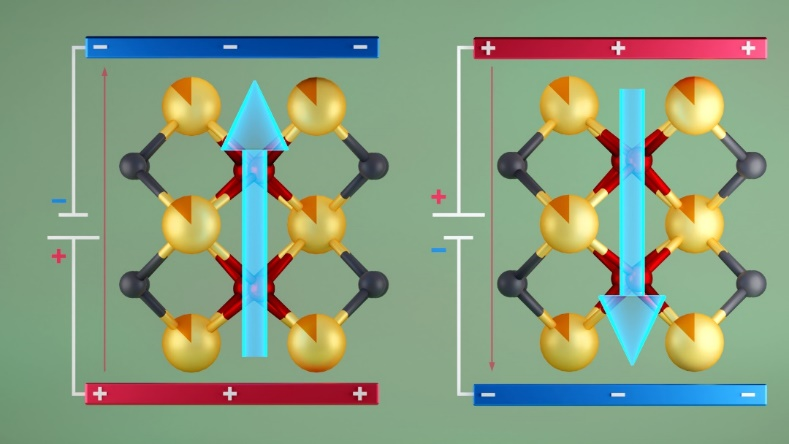
The first report of room temperature ferroelectricity in bulk hafnia could extend Moore’s Law for data storage.
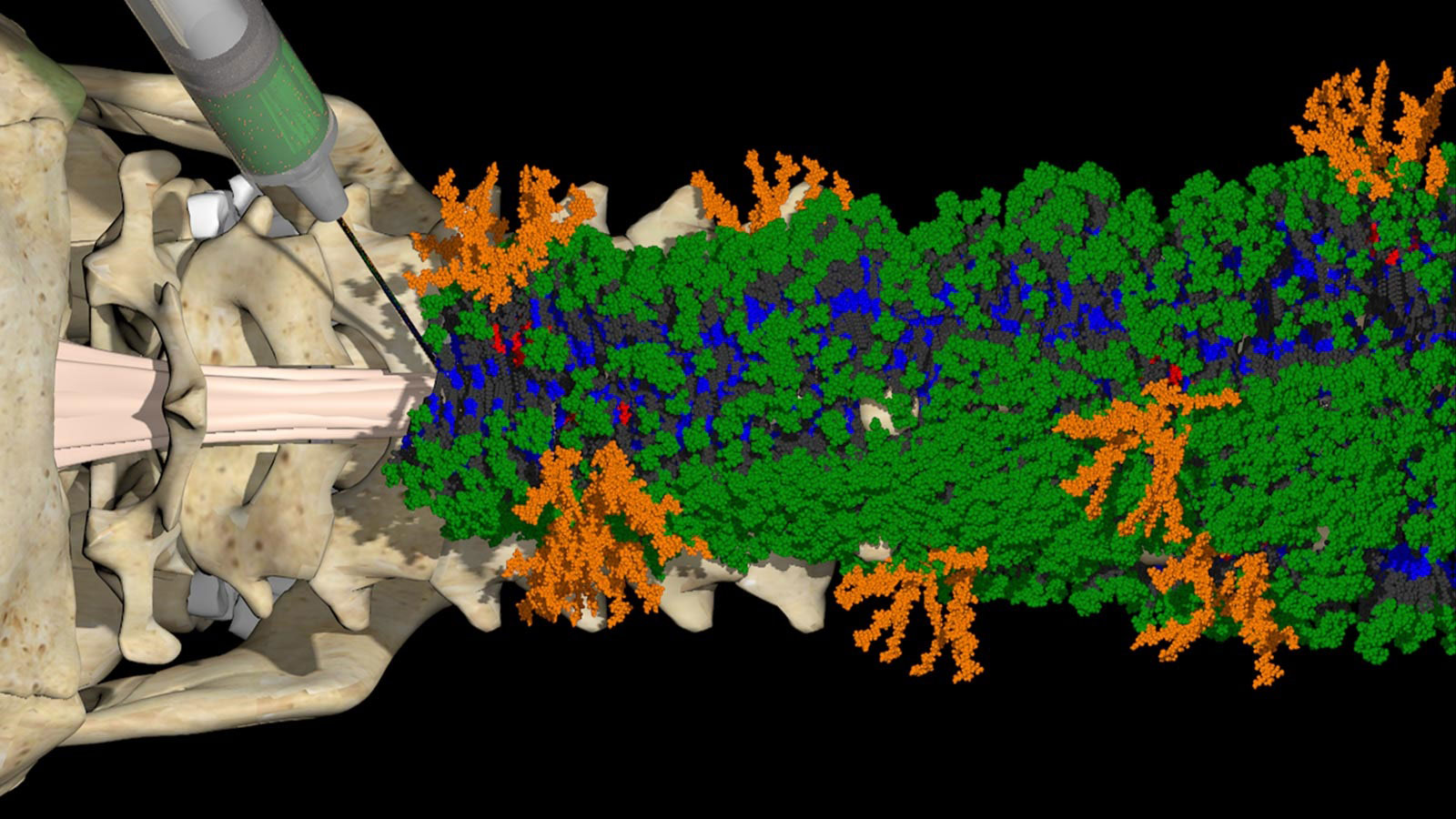
Paralyzed mice “walk” again after new treatment created with the aid of the Advanced Photon Source.
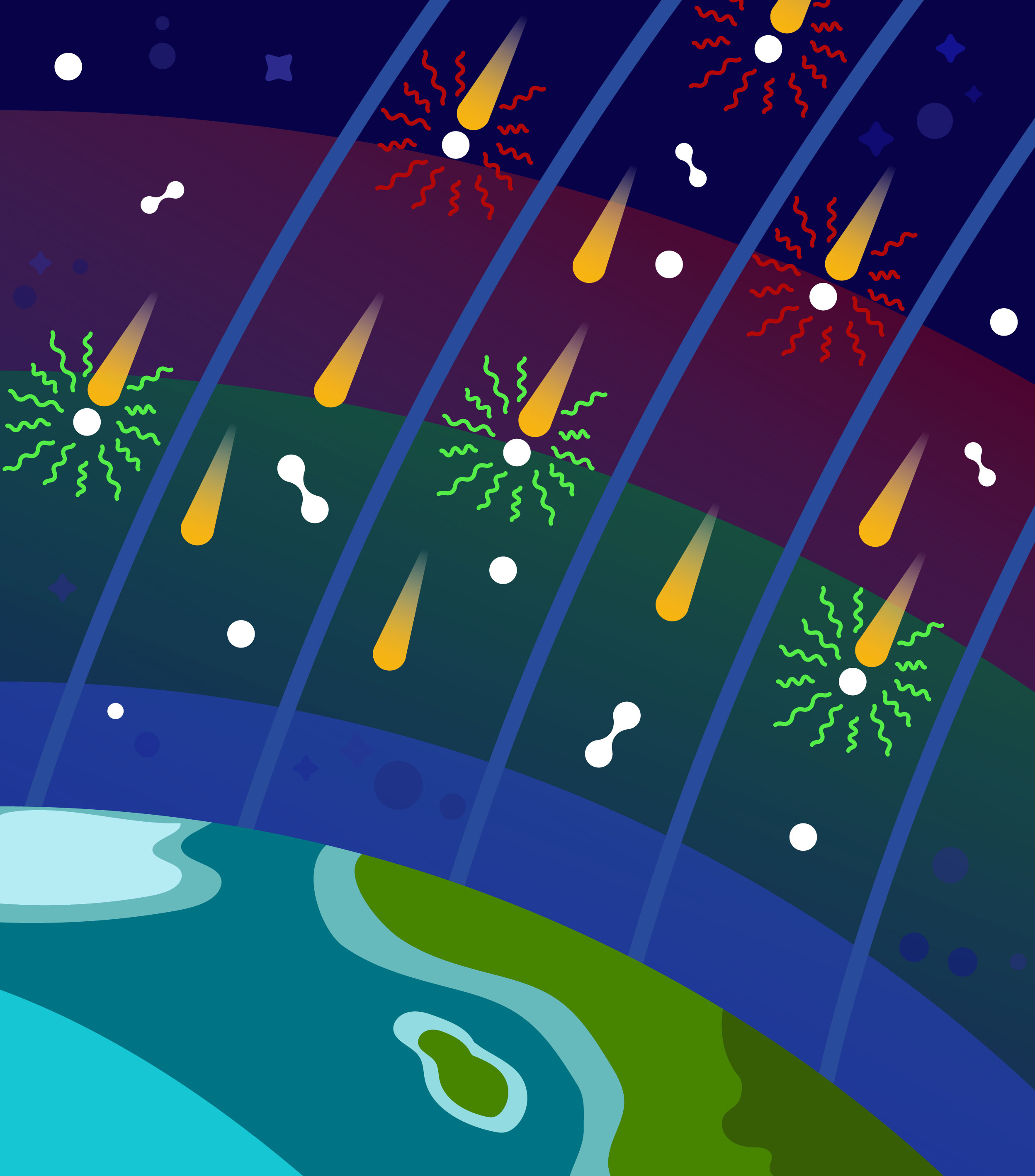

Laboratory measurements give new insights into the physics of auroral electron acceleration by Alfvén waves.
Researchers enable real-time adjustments to communication among three remote nodes in a quantum network.